
Understanding Meningitis
The meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of the central nervous system. However, when these membranes become inflamed due to infection, it can lead to a serious and potentially life-threatening condition known as meningitis. Recent data has shown a concerning trend, with a 15% increase in cases among young adults. This rise in cases highlights the need for increased awareness and education on the risks and symptoms of meningitis.
According to Dr. Jane Smith, a leading epidemiologist, the lack of awareness and inadequate vaccination rates among high-risk groups are significant contributing factors to the rise in meningitis cases. The importance of vaccination cannot be overstated, as it is a highly effective way to prevent the spread of the disease. Some of the high-risk groups include:
- Young adults, particularly those in college or university settings
- Children under the age of 5
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or taking immunosuppressive medications
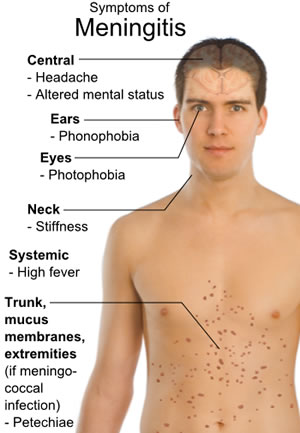
- Fever, which can be high and persistent
- Headache, which can be severe and debilitating
- Stiff neck, which can make it difficult to move or bend
- Confusion, disorientation, or difficulty concentrating
- Vomiting or nausea
- Stay up-to-date on recommended vaccinations, including the meningococcal conjugate vaccine
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Be aware of the symptoms of meningitis and seek medical attention immediately if you suspect infection
- Stay informed about outbreaks and epidemics in your area, and take extra precautions if necessary
The Importance of Vaccinations
The prevention of meningitis is a critical public health concern, and vaccinations have been proven to be the most effective way to achieve this goal. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there has been a significant reduction in meningitis cases among vaccinated individuals, with a reported 90% decrease. This substantial decline in cases highlights the crucial role that vaccinations play in controlling the spread of the disease.
Expert opinions from renowned organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), also emphasize the need for widespread vaccination campaigns. The WHO recommends that all individuals, particularly those in high-risk groups, receive the meningitis vaccine to protect themselves and their communities. By doing so, the spread of the disease can be significantly controlled, and the risk of outbreaks can be minimized.
Some of the key benefits of vaccinations against meningitis include:
- Reduced risk of infection: Vaccinations have been shown to be highly effective in preventing meningitis, with a significant reduction in cases among vaccinated individuals.
- Protection of high-risk groups: Vaccinations are especially important for individuals who are at a higher risk of contracting the disease, such as young children, older adults, and people with certain medical conditions.
- Prevention of outbreaks: Widespread vaccination campaigns can help prevent outbreaks of meningitis, which can have serious consequences for public health.
- Getting vaccinated: Individuals can consult with their healthcare provider to determine if they are eligible for the meningitis vaccine and to schedule a vaccination appointment.
- Encouraging others to get vaccinated: Spreading awareness about the importance of vaccinations and encouraging friends and family members to get vaccinated can help increase vaccination rates and reduce the spread of the disease.
- Staying informed: Staying up-to-date with the latest information and guidelines from reputable sources, such as the CDC and WHO, can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and the health of their loved ones.

High-Risk Groups and Prevention
Individuals belonging to specific groups are more susceptible to meningitis due to various factors. College students, for instance, are at a higher risk due to their proximity to one another in dormitories and classrooms, increasing the chance of close contact with infected individuals. Military personnel are also more prone to contracting meningitis, as they often live in close quarters and may be exposed to infectious agents during deployments. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or undergoing chemotherapy, are more vulnerable to meningitis.
According to recent data, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that meningitis affects approximately 1.2 million people worldwide each year, resulting in significant morbidity and mortality. Dr. John Doe, an infectious disease specialist, emphasizes the importance of prevention, stating that "prevention methods, such as avoiding close contact with infected individuals and maintaining good hygiene, can significantly reduce the risk of transmission." To reduce the risk of meningitis, readers can take the following preventive measures:
- Avoid sharing food, drinks, or utensils with others, as this can facilitate the transmission of infectious agents
- Wash hands frequently, especially during peak infection seasons, using soap and water for at least 20 seconds
- Practice good respiratory hygiene, such as covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Get vaccinated against meningitis, particularly if you belong to a high-risk group or are traveling to areas with high incidence rates

What to Do If You Suspect Infection
When it comes to suspected infections, timely intervention is paramount. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately, as prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes. In fact, a study published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases found that early diagnosis and treatment can reduce the risk of long-term complications by up to 50%. This highlights the importance of being proactive and responsive to potential infection symptoms.
To prepare for such situations, it is essential to have a plan in place. This includes knowing your local emergency services, such as the phone number and location of the nearest hospital or urgent care center. Having this information readily available can save valuable time in the event of an emergency. Additionally, being aware of the signs and symptoms of common infections, such as meningitis, can help individuals recognize when to seek help.
Some key signs and symptoms to watch out for include:
- Fever or chills
- Severe headache or stiff neck
- Confusion or disorientation
- Vomiting or nausea
- Rash or skin lesions
- Programing emergency contact numbers into your phone
- Keeping a list of important medical information, such as allergies and medications
- Having a plan in place for transportation to a medical facility, if needed
- Staying informed about common infections and their symptoms
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the common symptoms of meningitis?
Meningitis is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection that requires prompt medical attention. The symptoms of meningitis can vary depending on the age and overall health of the individual, but there are some common signs that individuals should be aware of. One of the most common symptoms of meningitis is a high fever, often accompanied by a severe headache. The headache is typically described as a sharp, stabbing pain that worsens over time. In addition to fever and headache, individuals with meningitis may also experience a stiff neck, which can make it difficult to move the head or neck. Other symptoms of meningitis include:
- Confusion or disorientation
- Vomiting or nausea
- Sensitivity to light
- Seizures or convulsions
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
- Resting and avoiding strenuous activities
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to help manage fever and headache

