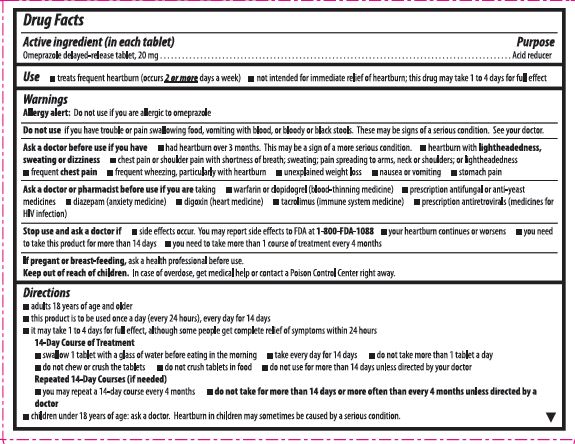
What is Omeprazole and How Does it Work?
Omeprazole is a widely prescribed medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). With over 10 million prescriptions written annually in the US, it is one of the most commonly used medications for treating acid-related disorders. By reducing stomach acid production, omeprazole provides relief from symptoms such as heartburn, bloating, and abdominal pain.
According to Dr. Sarah Jarvis, a renowned BBC doctor, omeprazole can be an effective treatment option for acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). However, its long-term use can lead to unwanted side effects. Some of the potential risks associated with omeprazole include:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Prolonged use of omeprazole can interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12, leading to deficiency and related health problems.
- Increased risk of osteoporosis: Long-term use of omeprazole can increase the risk of osteoporosis, particularly in older adults, due to impaired calcium absorption.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, exacerbating acid reflux symptoms.
- Avoiding trigger foods: Foods such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, and chocolate can trigger acid reflux in some individuals.
- Elevating the head of the bed: Raising the head of the bed by 6-8 inches can help reduce symptoms of acid reflux at night.

Potential Side Effects of Long-Term Omeprazole Use
Recent studies have shed light on the potential risks associated with long-term omeprazole use. A 2019 study published in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology found a 50% increased risk of kidney disease among patients taking omeprazole for an extended period. This alarming statistic highlights the importance of patients being aware of the potential side effects and taking proactive measures to mitigate them.
To minimize the risks, patients should be mindful of their kidney function and bone density while taking omeprazole. Dr. Jarvis recommends regular monitoring to detect any potential issues early on. Some key factors to consider include:
- Duration of treatment: The longer the treatment period, the higher the risk of kidney disease and other side effects.
- Dose and frequency: Taking higher doses or more frequent doses can increase the risk of adverse effects.
- Individual health factors: Patients with pre-existing kidney disease or osteoporosis may be more susceptible to the negative effects of long-term omeprazole use.
- H2 blockers: These medications can help reduce acid production in the stomach and may be a suitable alternative for some patients.
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids can provide quick relief for mild heartburn and acid reflux symptoms.
- Lifestyle modifications: Making dietary changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and eating smaller meals, can also help alleviate symptoms.

Alternative Treatment Options for Acid Reflux
Acid reflux is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort, pain, and disruption to daily life. Fortunately, recent studies have shown that lifestyle changes can play a significant role in alleviating symptoms. A 2020 study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology found that patients who made lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, dietary modifications, and stress reduction, experienced a 75% reduction in symptoms. This is a significant finding, highlighting the importance of holistic approaches to managing acid reflux.
To make effective lifestyle changes, it is essential to understand the key areas to focus on. Some of the most critical changes include:
- Weight loss: Excess weight can put pressure on the stomach, causing acid reflux. Losing weight can help alleviate symptoms.
- Dietary modifications: Avoiding trigger foods and eating smaller, more frequent meals can help reduce symptoms.
- Stress reduction: Stress can exacerbate acid reflux symptoms. Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help manage stress.
- Elevating the head of their bed by 6-8 inches to prevent stomach acid from flowing up into the esophagus
- Avoiding trigger foods, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, and chocolate, which can exacerbate symptoms
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals to reduce pressure on the stomach

What to Do If You're Taking Omeprazole for Acid Reflux
When managing acid reflux with omeprazole, it's crucial to have an open and informed discussion with your doctor. A 2018 study published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine found that only 50% of patients were aware of the potential side effects associated with long-term omeprazole use. This lack of awareness highlights the importance of consulting your doctor to understand the potential risks and benefits of omeprazole treatment.
To maximize the effectiveness of your treatment plan, Dr. Jarvis recommends keeping a symptom journal to track your progress. This involves recording the frequency and severity of your acid reflux symptoms, as well as any changes you notice after starting omeprazole. By monitoring your symptoms, you can identify patterns and adjust your treatment plan as needed. Some key factors to track in your symptom journal include:
- Frequency and severity of acid reflux symptoms
- Time of day when symptoms occur
- Triggers that exacerbate symptoms, such as certain foods or activities
- Any changes in symptoms after starting omeprazole
- Dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods or following a low-acid diet
- Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, quitting smoking, or reducing stress
- Alternative medications or therapies, such as histamine-2 (H2) blockers or proton pump inhibitors
- Natural remedies, such as ginger or melatonin, which may help alleviate acid reflux symptoms

