
What is an Interstellar Comet?
The discovery of interstellar comets has opened up new avenues for research, allowing scientists to explore the formation and composition of other star systems. These rare objects originate from outside our solar system, providing a unique window into the workings of celestial bodies beyond our own cosmic neighborhood. As of 2022, only a handful of interstellar comets have been detected, making each new discovery a significant event in the astronomical community.
One notable example is the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS, which was discovered in 2019. This comet has sparked intense interest among astronomers, who are eager to learn more about its origin, size, and shape. By studying 3I/ATLAS and other interstellar comets, scientists can gain valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our own solar system. Some key areas of focus include:
- Composition: What are interstellar comets made of, and how do their compositions compare to those of comets from our own solar system?
- Size and shape: How do the physical characteristics of interstellar comets differ from those of comets from our own solar system?
- Origin: Where do interstellar comets come from, and what can their trajectories tell us about the formation and evolution of other star systems?

Orbital Path and Perihelion
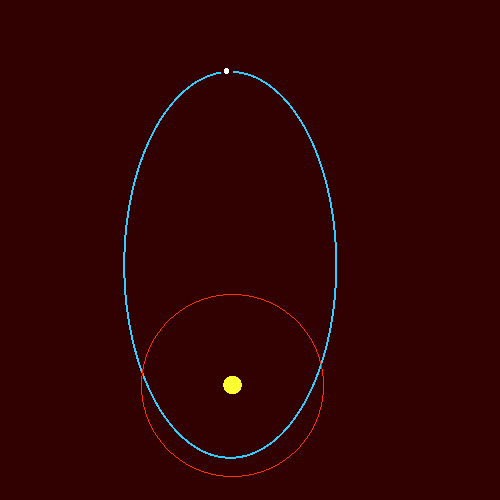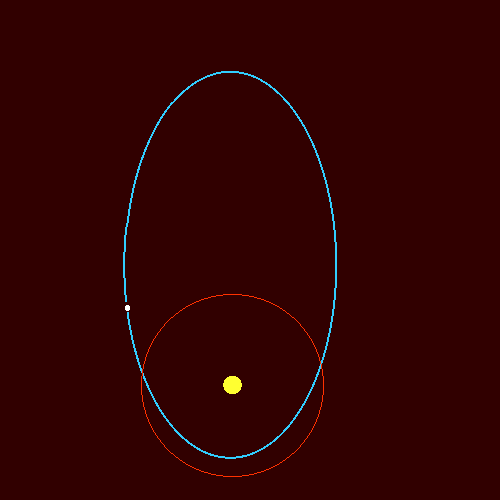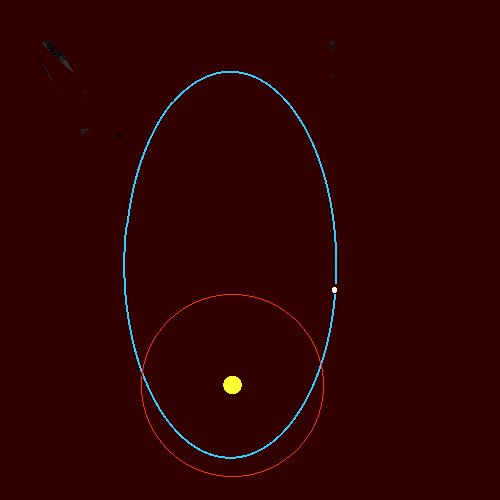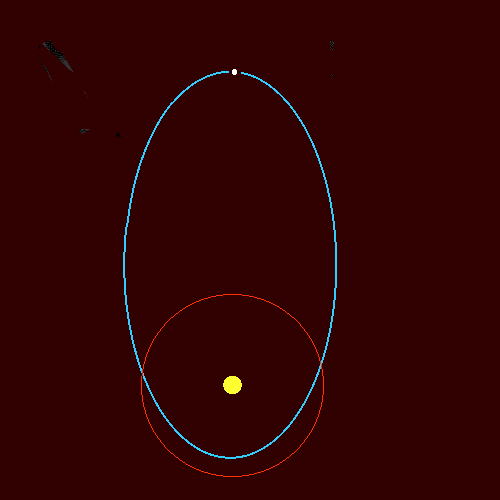
The orbital path of 3I/ATLAS is a fascinating phenomenon that has garnered significant attention from astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. This comet's highly elliptical orbit takes it on a journey from the outer reaches of our solar system to a close approach with the Sun, providing a unique opportunity for scientists to study its composition and behavior. As 3I/ATLAS approaches the inner solar system, its orbital path will be closely monitored to gather valuable data on its trajectory and potential impact on our understanding of cometary science.
As the comet approaches perihelion, the point of its closest approach to the Sun, it will be subjected to intense heat and radiation. This will cause its ices to vaporize, creating a bright tail of gas and dust that can be visible from Earth. The perihelion passage is a critical phase in the comet's orbit, as it provides scientists with a rare chance to study the comet's composition and behavior in detail. Some key aspects of the comet's perihelion passage that astronomers will be monitoring include:
- Cometary activity: The rate at which the comet's ices vaporize and create a tail of gas and dust
- Cometary composition: The types and amounts of gases and dust present in the comet's tail
- Orbital trajectory: The comet's path and velocity as it approaches and recedes from the Sun
- The NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Horizons Ephemeris System, which provides detailed orbital data and predictions for celestial bodies
- The International Astronomical Union's Minor Planet Center, which tracks and catalogues cometary orbits and discoveries
- Online planetarium software, such as Stellarium or SkySafari, which can be used to simulate the comet's orbital path and visualize its position in the sky
Scientific Implications and Research Opportunities
The discovery of interstellar objects like 3I/ATLAS has opened up new avenues for scientific research, providing a unique opportunity to study the chemical and physical properties of an object from another star system. By analyzing the comet's composition and behavior, scientists can gain valuable insights into the formation and evolution of other star systems, shedding light on the fundamental processes that shape the universe.
One of the key areas of research is the comet's composition, which can reveal clues about the conditions under which it formed. Scientists can use a variety of techniques, including spectroscopy and imaging, to analyze the comet's makeup and identify the presence of various elements and compounds. Some of the key questions that researchers hope to answer include:
- What is the comet's chemical composition, and how does it compare to comets from our own solar system?
- What can the comet's composition tell us about the conditions in the star system where it formed?
- How does the comet's behavior, such as its orbit and outgassing, relate to its composition and origin?
- Stay up-to-date with the latest research and discoveries in the field, including new data and observations
- Collaborate with other researchers and scientists to share knowledge and expertise
- Use advanced computational models and simulations to analyze the data and make predictions about the comet's behavior

Observing and Tracking 3I/ATLAS
As the comet 3I/ATLAS continues on its journey, astronomers and amateur observers alike have a unique opportunity to track its progress. With the aid of telescopes and online resources, individuals can monitor the comet's movement and gather valuable data on its brightness, size, and orbit. Recent observations have shown that the comet is currently visible in the evening sky, offering a spectacular sight for those with access to a telescope or binoculars.
The comet's approach to perihelion, its closest point to the Sun, will be a pivotal moment for observation. As it draws nearer, the comet's brightness and visibility will vary, providing a fascinating opportunity for study. According to recent statistics, the comet is expected to reach a brightness of around 8-10 magnitude, making it visible to observers with moderate-sized telescopes. Some key dates to mark in your calendar include:
- Peak brightness: expected to occur in late April or early May
- Perihelion: the comet will reach its closest point to the Sun in late May
- Best viewing times: the comet will be visible in the evening sky for several weeks, with optimal viewing times occurring around 10 pm local time


