Jane Goodall's remarkable life and legacy have left an indelible mark on the world of wildlife conservation and research. As a pioneering primate expert, she has dedicated her life to studying and protecting animals, particularly chimpanzees. Her groundbreaking research in Tanzania's Gombe Stream National Park has greatly advanced our understanding of these intelligent and social creatures.
Throughout her career, Goodall has been a tireless advocate for wildlife conservation and environmental protection. Her work has taken her to various parts of the world, from the lush forests of Africa to the corridors of power in governments and international organizations. She has worked with world leaders, scientists, and local communities to promote the preservation of natural habitats and the welfare of animals.
Some of the key aspects of Jane Goodall's legacy include:
- Her pioneering research on chimpanzees, which has greatly advanced our understanding of their behavior, social structures, and intelligence
- Her tireless advocacy for wildlife conservation and environmental protection, which has inspired a generation of conservationists and researchers
- Her work with local communities and governments to promote sustainable development and conservation practices
- Her dedication to promoting the welfare and protection of animals, particularly those that are endangered or vulnerable
Goodall's legacy extends beyond her scientific contributions and advocacy work. She has also inspired countless people around the world with her courage, compassion, and determination. Her story has been an inspiration to many, and her work continues to be a beacon of hope for a better future for all living creatures. Her remarkable life and legacy serve as a testament to the power of dedication, hard work, and passion for making a positive impact on the world.

Early Life and Career
Jane Goodall was born on April 3, 1934, in London, England, to Mortimer Herbert Morris-Goodall and Vanne Morris-Goodall. Her early life was marked by a deep fascination with the natural world, which was encouraged by her mother. Goodall's love for animals and the outdoors was evident from a young age, and she spent much of her childhood reading about and observing the wildlife in her neighborhood.
Goodall's interest in animals led her to dream of traveling to Africa to study them in their natural habitat. After completing her secondary education, she worked as a secretary and later as a waitress to save money for her trip. In 1957, she finally had the opportunity to visit a friend's farm in Kenya, where she met the famous anthropologist Louis Leakey. This meeting would change the course of her life and set her on the path to becoming a renowned researcher.
In 1960, Leakey appointed Goodall to study chimpanzees in Tanzania's Gombe Stream National Park. At the time, very little was known about chimpanzees, and Goodall's research would go on to revolutionize the field of primatology. Some of the key aspects of her research in Gombe Stream National Park include:
- Observing and recording the behavior of chimpanzees in their natural habitat
- Discovering the use of tools by chimpanzees, such as using sticks to extract termites for food
- Documenting the complex social structures and behaviors of chimpanzees, including their communication methods and conflict resolution strategies
Goodall's groundbreaking research in Gombe Stream National Park spanned several decades and has had a profound impact on our understanding of chimpanzees and their place in the natural world.
Goodall's work in Tanzania not only advanced the field of primatology but also raised important questions about conservation and the protection of endangered species. Her research highlighted the need for responsible stewardship of the natural world and inspired a new generation of scientists, conservationists, and animal lovers. Through her tireless advocacy and dedication to her work, Goodall has become an iconic figure in the world of science and conservation.

Contributions to Primatology
Jane Goodall's groundbreaking work in primatology has significantly advanced our knowledge of chimpanzees and their behavior. Her extensive research in Gombe Stream National Park, Tanzania, has provided invaluable insights into the complex social structures of chimpanzees. Goodall's observations have shown that chimpanzees live in large communities with a strict hierarchy, led by dominant males. These communities are often divided into smaller groups, with females playing a crucial role in maintaining social bonds.
One of the most significant discoveries made by Goodall was the use of tools among chimpanzees. She observed that chimpanzees use sticks to extract termites from their mounds, rocks to crack open nuts, and leaves as sponges to soak up water. This discovery challenged the long-held belief that humans were the only species capable of using tools. Goodall's findings have been widely accepted and have far-reaching implications for our understanding of animal cognition and intelligence.
The impact of Goodall's research on our understanding of human evolution is profound. Her work has shown that chimpanzees and humans share many similarities in behavior and social structures. Some of the key similarities include:
- Complex social behaviors, such as cooperation and altruism
- Use of tools and technology to adapt to their environment
- Emotional intelligence, including emotions such as joy, sadness, and empathy
- Cultural behaviors, such as learning and transmitting knowledge from one generation to the next
These similarities suggest that humans and chimpanzees shared a common ancestor and that many of our behaviors and social structures have evolved from those of our primate ancestors.
Goodall's research has also highlighted the importance of conservation and protection of chimpanzee habitats. As their habitats are destroyed and fragmented, chimpanzees are facing numerous threats, including poaching, disease, and climate change. Goodall's work has raised awareness about the need to protect these incredible creatures and their habitats, not just for their sake, but also for the sake of our own understanding of human evolution and our place in the natural world.
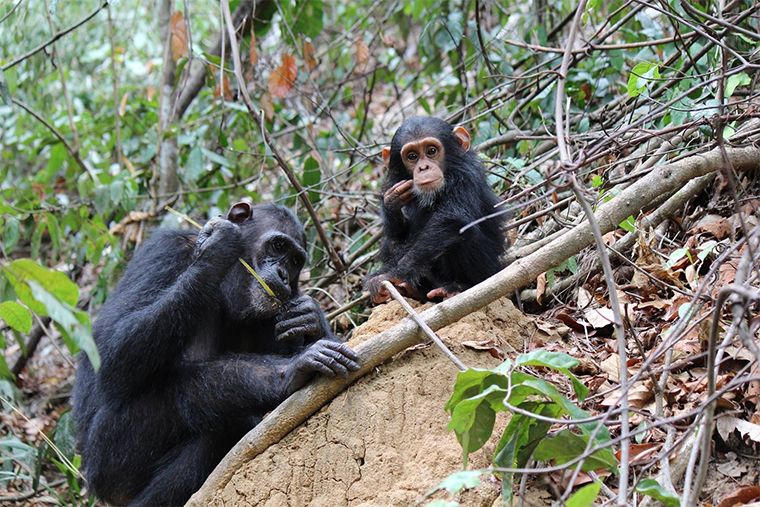

Wildlife Conservation and Advocacy
Jane Goodall is a renowned wildlife conservationist who has dedicated her life to protecting chimpanzees and their habitats. Her groundbreaking research in Tanzania's Gombe Stream National Park has greatly advanced our understanding of these intelligent and social animals. Goodall's tireless efforts to protect chimpanzees have taken her from the forests of Africa to the halls of international conferences, where she advocates for their welfare and conservation.
Her work with organizations such as the Jane Goodall Institute has been instrumental in promoting wildlife conservation and advocacy. The institute supports research, education, and community-based conservation programs, with a focus on protecting chimpanzees and their habitats. Goodall's collaboration with the institute has helped to raise awareness about the importance of conservation and the need to protect endangered species.
Some of the key areas of focus for Goodall's advocacy work include:
- Protecting chimpanzees from habitat loss and fragmentation
- Preventing the capture and trade of chimpanzees for the pet and entertainment industries
- Promoting sustainable livelihoods for communities living near chimpanzee habitats
- Supporting research and monitoring programs to better understand chimpanzee behavior and ecology
These efforts have contributed significantly to the development of effective conservation strategies and the protection of chimpanzee populations.
Goodall's advocacy for animal welfare and environmental conservation extends beyond her work with chimpanzees. She is a vocal advocate for the protection of all animals, and has spoken out against animal cruelty, deforestation, and climate change. Her message of hope and urgency has inspired countless people around the world to take action on behalf of the environment and the animals that inhabit it. Through her writing, speaking, and activism, Goodall continues to inspire a new generation of conservationists and advocates for wildlife protection.
Legacy and Impact
The groundbreaking research conducted by Jane Goodall has left an indelible mark on the field of primatology. Her tireless efforts to study chimpanzees in their natural habitat have greatly expanded our understanding of these intelligent and social creatures. Goodall's findings have not only rewritten the textbooks on primatology but have also inspired a new generation of researchers to pursue careers in this field.
Her inspiration to future generations of scientists and conservationists cannot be overstated. Goodall's passion and dedication to her work have motivated countless individuals to pursue careers in science, conservation, and animal welfare. Many have followed in her footsteps, conducting research and working to protect endangered species and their habitats.
- Her work has also raised awareness about the importance of conservation and the need to protect our planet's precious wildlife and ecosystems.
- Goodall's legacy extends far beyond the scientific community, with her message of compassion, empathy, and stewardship resonating with people from all walks of life.
The continued relevance of her work in modern conservation efforts is a testament to the enduring power of Goodall's research. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, habitat destruction, and species extinction, Goodall's findings remain a vital component of conservation strategies. Her work has highlighted the intricate relationships between species and their environments, demonstrating the need for a holistic approach to conservation.
- By studying the complex social dynamics of chimpanzees, researchers can gain valuable insights into the behavior and ecology of other species.
- Goodall's research has also underscored the importance of community-led conservation initiatives, which empower local people to take ownership of conservation efforts and work towards sustainable solutions.
In conclusion, the lasting influence of Goodall's research is a shining example of the impact one person can have on the world. Her work continues to inspire and motivate people around the globe, driving efforts to protect the natural world and promote a culture of compassion and stewardship. As we look to the future, it is clear that Goodall's legacy will endure, guiding generations to come in their pursuit of a more sustainable and harmonious relationship between humans and the environment.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What was Jane Goodall's most significant contribution to science?
Jane Goodall's groundbreaking research in the field of primatology has left an indelible mark on the scientific community. Her pioneering work with chimpanzees has greatly expanded our knowledge of these fascinating creatures and their behavior. One of the most significant aspects of her research was the discovery of tool use among chimpanzees. This finding has far-reaching implications for our understanding of human evolution and animal cognition.
The observation of chimpanzees using tools, such as sticks and rocks, to extract food and solve problems challenged the long-held notion that humans were the only species capable of using tools. This discovery has led to a reevaluation of the cognitive abilities of non-human animals and their place in the evolutionary tree. Goodall's research has shown that chimpanzees are capable of complex problem-solving and innovation, traits that were previously thought to be unique to humans.
Some of the key findings from Goodall's research include:
- Chimpanzees using sticks to extract termites from their mounds for food
- Chimpanzees using rocks to crack open nuts and seeds
- Chimpanzees using leaves as sponges to soak up water
These observations have demonstrated that chimpanzees are capable of adapting to their environment and using tools to overcome challenges. This level of cognitive ability has significant implications for our understanding of human evolution and the development of tool use in early humans.
Goodall's research has also highlighted the importance of conservation and protection of chimpanzee habitats. As our understanding of these animals has grown, so has our appreciation for their intelligence and social complexity. Efforts to protect and preserve chimpanzee populations are crucial for maintaining the health and diversity of ecosystems. By continuing to study and learn from these incredible animals, we can gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and our place within it.
What is the Jane Goodall Institute, and what does it do?
The Jane Goodall Institute is a global organization dedicated to protecting chimpanzees and their habitats, while also promoting conservation and sustainability. This organization was founded by Dr. Jane Goodall, a renowned primatologist and conservationist, who is known for her groundbreaking research on chimpanzees.
The institute's mission is to advance the well-being of chimpanzees, other animals, and the environment by promoting conservation, education, and research. The organization works to protect chimpanzee habitats and prevent their extinction, while also supporting local communities and promoting sustainable livelihoods.
Some of the key areas of focus for the institute include:
- Conservation efforts, such as protecting and restoring chimpanzee habitats, and reducing human-chimpanzee conflict
- Research and monitoring, including studying chimpanzee behavior and population dynamics
- Education and outreach, such as providing educational programs and materials for schools and communities
- Community engagement and support, including working with local communities to develop sustainable livelihoods and promote conservation
The institute also supports the rehabilitation and care of orphaned or injured chimpanzees, and works to combat the illegal trade in chimpanzees and other wildlife. By working to protect chimpanzees and their habitats, the institute is also helping to preserve biodiversity and promote ecosystem health.
Overall, the Jane Goodall Institute plays a critical role in promoting conservation and sustainability, and is an important voice for the protection of chimpanzees and the environment. Through its work, the institute is helping to create a more sustainable future for all, and is inspiring others to join in the effort to protect our planet and its inhabitants.
How can I get involved in wildlife conservation, inspired by Jane Goodall's legacy?
Jane Goodall's groundbreaking research and tireless advocacy have inspired countless individuals to take action in protecting the natural world. For those looking to make a difference, there are numerous ways to get involved in wildlife conservation. One of the most effective ways to contribute is by volunteering with organizations dedicated to conservation efforts. This can include participating in local clean-up initiatives, assisting with wildlife rehabilitation centers, or joining international conservation projects.
Volunteering not only provides hands-on experience but also offers a unique opportunity to learn from experts in the field. Many organizations, such as the Jane Goodall Institute, offer volunteer programs that cater to diverse interests and skill levels. By lending a hand, individuals can help make a tangible impact on conservation efforts while gaining valuable knowledge and skills.
In addition to volunteering, reducing one's environmental impact is crucial in supporting conservation efforts. This can be achieved by making conscious choices in daily life, such as:
- Reducing meat consumption and choosing sustainable food options
- Using public transport, cycling, or walking instead of driving
- Conserving water and reducing energy consumption
- Avoiding products with palm oil and other environmentally harmful ingredients
- Supporting eco-friendly policies and practices in the community
These small changes can collectively make a significant difference in mitigating the impact of human activities on the environment.
Staying informed about wildlife conservation issues is also essential in making a positive impact. This can be done by:
- Following reputable conservation organizations and news outlets
- Participating in online forums and discussions
- Attending workshops, lectures, and community events
- Reading books and articles on conservation topics
- Supporting conservation-focused documentaries and films
By staying up-to-date on the latest conservation issues and research, individuals can better understand the complexities of wildlife conservation and make informed decisions in their daily lives.
Ultimately, every individual has the power to contribute to wildlife conservation, and collective action can lead to significant positive change. By volunteering, reducing their environmental impact, and staying informed, individuals can help protect the natural world and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.