The Earth's magnetic field plays a vital role in our daily lives, and its significance cannot be overstated. It is a complex and dynamic force that affects our planet in numerous ways. From protecting us from harmful solar and cosmic radiation to facilitating navigation and communication, the Earth's magnetic field is an essential component of our daily existence.
One of the primary functions of the Earth's magnetic field is to shield us from the adverse effects of solar and cosmic radiation. This radiation can have devastating consequences for our health, technology, and environment. The magnetic field acts as a protective barrier, deflecting and absorbing these harmful rays, thereby safeguarding our well-being and the integrity of our technological systems.
The importance of the Earth's magnetic field can be seen in various aspects of our lives, including:
- Navigation: The magnetic field provides a reference point for navigation, allowing us to determine our direction and location with precision.
- Communication: The magnetic field plays a crucial role in facilitating communication, particularly in the transmission of radio signals and satellite communications.
- Climate regulation: The magnetic field influences the Earth's climate by controlling the amount of solar radiation that enters our atmosphere.
- Geological processes: The magnetic field is involved in various geological processes, such as plate tectonics and the formation of minerals.
In addition to these functions, the Earth's magnetic field has a significant impact on our technological infrastructure. Many of our modern technologies, such as GPS, satellite communications, and power grids, rely on the magnetic field to operate efficiently. Any disruptions to the magnetic field can have far-reaching consequences for our technological systems and our daily lives.
Overall, the Earth's magnetic field is a vital component of our planet's ecosystem, and its importance cannot be overstated. Its role in protecting us from harm, facilitating navigation and communication, and influencing the Earth's climate and geological processes makes it an essential aspect of our daily lives.
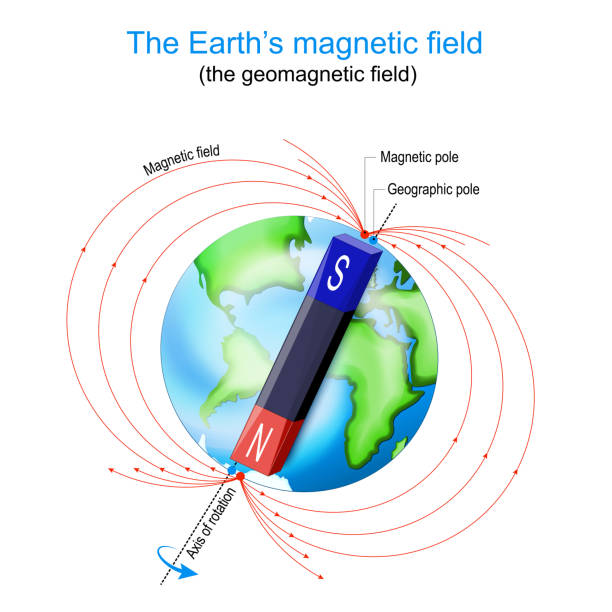
What is Earth's Magnetic Field?
The Earth's magnetic field is a complex and dynamic phenomenon that plays a crucial role in protecting our planet from harm. At its core, the magnetic field is a region around the Earth where magnetic forces can be detected. It is generated by the movement of molten iron in the Earth's core, which creates electric currents that produce the magnetic field.
The movement of molten iron in the Earth's core is responsible for generating the magnetic field. This movement creates electric currents, which in turn produce the magnetic field. The Earth's core is made up of two layers: a solid inner core and a liquid outer core. The liquid outer core is where the molten iron is located, and it is this movement that generates the magnetic field.
The magnetic field has several important functions, including:
- Protecting the planet from harmful solar and cosmic radiation
- Guiding migratory animals and helping them navigate
- Influencing the Earth's climate and weather patterns
- Shaping the Earth's magnetosphere, which is the region around the Earth where the magnetic field dominates
The protection of the planet from harmful radiation is one of the most important functions of the magnetic field. The magnetic field acts as a shield, deflecting charged particles from the sun and deep space, and preventing them from entering the Earth's atmosphere.
The Earth's magnetic field is not constant and has changed over time. The field has reversed many times in the Earth's history, with the North Pole becoming the South Pole and vice versa. These reversals have occurred at irregular intervals, with the most recent reversal occurring about 780,000 years ago. Understanding the Earth's magnetic field and its role in protecting the planet is essential for understanding the Earth's history and its place in the universe.
The study of the Earth's magnetic field is an active area of research, with scientists working to understand the complex processes that generate and maintain the field. By studying the magnetic field, scientists can gain insights into the Earth's internal dynamics and the processes that shape our planet. This knowledge can also be used to better understand the Earth's history and to predict future changes in the magnetic field.

Navigation and Technology
The magnetic field plays a vital role in various navigation systems, including GPS and compasses. GPS relies on a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, which transmit signals that can be received by GPS receivers on the ground. These signals contain information about the satellite's location and the current time, allowing the receiver to calculate its own location. The magnetic field is used to determine the orientation of the GPS receiver, which is essential for accurate navigation.
The magnetic field is also used in compasses, which are simple navigation tools that indicate direction. A compass works by aligning a magnetized needle with the Earth's magnetic field, allowing the user to determine their direction. This technology has been used for centuries and is still an essential tool for navigation today. The use of the magnetic field in navigation systems has revolutionized the way we travel and explore the world.
The impact of the magnetic field on satellite communications and electronic devices is significant. Satellites use the magnetic field to maintain their orientation and stability in space. Electronic devices, such as smartphones and laptops, also use the magnetic field to determine their location and orientation. This information is used to provide location-based services, such as mapping and navigation. The magnetic field also affects the performance of electronic devices, particularly those that use magnetically sensitive components.
Some of the key applications of the magnetic field in navigation and technology include:
- GPS navigation systems
- Compasses and directional finding
- Satellite communications and orientation
- Electronic devices and location-based services
- Geological surveying and mineral exploration
The role of the magnetic field in geological surveying and mineral exploration is also significant. Geologists use the magnetic field to map the subsurface structure of the Earth and locate mineral deposits. This is done by measuring the variations in the magnetic field caused by different rock types and mineral deposits. The magnetic field can also be used to detect buried features, such as faults and fractures, which can be important for mineral exploration and geological surveying. By using the magnetic field, geologists can gain a better understanding of the Earth's subsurface structure and locate potential mineral deposits.
Effects on Climate and Weather
The Earth's magnetic field plays a significant role in shaping our climate and weather patterns. Research has shown that there is a correlation between the magnetic field and climate change. The magnetic field affects the amount of solar radiation that enters the Earth's atmosphere, which in turn influences global temperatures. Changes in the magnetic field can also impact the formation of clouds and precipitation patterns, leading to variations in regional weather conditions.
The relationship between the magnetic field and climate change is complex and multifaceted. Studies have found that changes in the magnetic field can influence the formation of clouds by affecting the amount of cosmic radiation that reaches the Earth's atmosphere. This can have a significant impact on global temperatures, as clouds play a crucial role in regulating the amount of solar radiation that enters the atmosphere.
- Changes in cloud cover can also impact precipitation patterns, leading to droughts or floods in certain regions.
- The magnetic field can also influence the formation of high and low-pressure systems, which can impact regional weather patterns.
- Furthermore, the magnetic field can affect the movement of jet streams, which can have a significant impact on global weather patterns.
The magnetic field influences the formation of clouds and precipitation patterns in several ways. For example, changes in the magnetic field can impact the amount of ice nucleation in clouds, which can affect the formation of precipitation. Additionally, the magnetic field can influence the movement of water vapor in the atmosphere, which can impact the formation of clouds and precipitation patterns.
- The magnetic field can also impact the amount of aerosols in the atmosphere, which can affect the formation of clouds and precipitation patterns.
- Changes in the magnetic field can also influence the formation of thunderstorms and other severe weather events.
- The magnetic field can also affect the movement of weather patterns, such as the movement of high and low-pressure systems.
A weakened magnetic field can have a significant impact on global weather patterns. If the magnetic field were to weaken significantly, it could lead to changes in cloud cover and precipitation patterns, resulting in more extreme weather events.
- A weakened magnetic field could also impact the formation of high and low-pressure systems, leading to changes in regional weather patterns.
- Changes in the magnetic field can also affect the movement of jet streams, which can have a significant impact on global weather patterns.
- Furthermore, a weakened magnetic field could also impact the amount of solar radiation that enters the Earth's atmosphere, leading to changes in global temperatures.

What if the Magnetic Field Disappeared?
The Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in protecting the planet from harmful solar and cosmic radiation. A sudden loss of the magnetic field would have severe consequences, including increased radiation exposure for both humans and wildlife. This could lead to a higher risk of cancer, genetic mutations, and other health problems. The increased radiation would also have a devastating impact on the Earth's ecosystem, potentially leading to the extinction of many species.
The disappearance of the magnetic field would also disrupt navigation and communication systems, which rely on the field to function properly. This would have a significant impact on global commerce, transportation, and communication. For example, satellite communications, GPS, and radio navigation would be severely disrupted, making it difficult for aircraft and ships to navigate. The consequences of such disruptions would be far-reaching, affecting many aspects of modern life.
Some of the potential consequences of a magnetic field disappearance include:
- Disruption of power grids and communication systems
- Increased risk of radiation exposure for astronauts and people in space
- Disruption of the Earth's climate, potentially leading to extreme weather events
- Impact on the Earth's geology, potentially leading to increased volcanic activity
The impact on the Earth's climate would be significant, as the magnetic field helps to regulate the amount of solar radiation that enters the atmosphere. Without the magnetic field, the Earth's climate could become more extreme, with higher temperatures and more frequent natural disasters.
The possibility of life on Earth adapting to a magnetic field-free environment is a topic of ongoing debate. While some scientists believe that life could adapt to such an environment, others argue that the consequences would be too severe. The Earth's geology would also be affected, potentially leading to increased volcanic activity and the formation of new mountain ranges. The long-term effects of a magnetic field disappearance would be catastrophic, and it is unlikely that life on Earth could adapt quickly enough to survive.
In the event of a magnetic field disappearance, the Earth's geology would undergo significant changes. The increased radiation would lead to the formation of new minerals and rocks, and the planet's geological activity would increase. The consequences of such changes would be far-reaching, affecting the Earth's ecosystem and potentially leading to the extinction of many species. The possibility of life on Earth adapting to such an environment is a complex and multifaceted topic, and one that requires further research and study.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What would happen to our technology if the magnetic field disappeared?
The Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in our daily lives, and its disappearance would have far-reaching consequences. One of the primary concerns is the impact on navigation systems. The magnetic field serves as a guide for compasses, GPS, and other navigation tools, allowing us to determine our direction and location. Without it, these systems would be severely disrupted, making it challenging to navigate, especially for aircraft, ships, and other vehicles that rely heavily on magnetic navigation.
The disruption to communication systems would also be significant. The magnetic field helps to protect communication signals from interference and disruption. Without it, radio signals and other forms of communication would be more susceptible to interference, making it difficult to transmit and receive information. This would have a major impact on global communication networks, including satellite communications, internet connectivity, and mobile phone networks.
The loss of the magnetic field could also potentially damage electronic devices. The magnetic field helps to shield the Earth from harmful solar and cosmic radiation, which can damage electronic components. Without this protection, electronic devices would be more vulnerable to radiation damage, which could lead to malfunctions, data loss, and even complete system failures. Some of the key areas that could be affected include:
- Computer systems and data storage devices
- Telecommunication equipment and networks
- Medical equipment and devices
- Aerospace and defense systems
The consequences of a magnetic field disappearance would be widespread and have a significant impact on our daily lives. It would require a major overhaul of our navigation and communication systems, as well as the development of new technologies to protect electronic devices from radiation damage. The effects would be felt across various industries, including aviation, maritime, healthcare, and finance, making it essential to understand the potential risks and consequences of such an event.
Can the Earth's magnetic field be restored if it disappears?
The Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in protecting our planet from harmful solar and cosmic radiation. It is generated by the movement of molten iron in the Earth's core, a process known as geodynamo. This movement creates electric currents, which in turn produce the magnetic field. The Earth's magnetic field is essential for navigation, communication, and even the formation of the Earth's climate.
The possibility of the Earth's magnetic field disappearing is a topic of ongoing research and debate. While it is unlikely that the magnetic field will disappear completely, there is evidence that it has weakened over time. This weakening has significant implications for our planet's ability to protect itself from external radiation. If the magnetic field were to disappear, the effects on the Earth's climate and ecosystem could be catastrophic.
Some of the key factors that contribute to the Earth's magnetic field include:
- the movement of molten iron in the Earth's core
- the Earth's rotation and orbit around the sun
- the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field and the solar wind
These factors work together to generate and maintain the Earth's magnetic field. However, if the magnetic field were to disappear, it is unlikely that it could be restored.
The reason for this is that the Earth's magnetic field is a self-sustaining process. The movement of molten iron in the core creates the magnetic field, which in turn helps to maintain the movement of the molten iron. If the magnetic field were to disappear, the movement of the molten iron would likely cease, making it difficult to restore the magnetic field. Additionally, the Earth's magnetic field is a complex system that is influenced by many factors, making it challenging to replicate or restore if it were to disappear.
In conclusion, while the Earth's magnetic field is essential for our planet's protection and stability, it is unlikely that it can be restored if it disappears completely. The complex processes that generate and maintain the magnetic field make it a unique and self-sustaining system that is difficult to replicate or restore. As such, it is essential to continue monitoring and researching the Earth's magnetic field to better understand its behavior and potential risks.
Is the Earth's magnetic field weakening, and what are the consequences?
The Earth's magnetic field has been a vital component of our planet's defense system, protecting us from harmful solar and cosmic radiation. However, recent studies have shown that this field has been weakening over the past few centuries. This decline has significant implications for the planet's climate and navigation systems.
One of the primary concerns is the potential impact on climate. The Earth's magnetic field plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of solar radiation that enters the atmosphere. As the field weakens, more radiation could penetrate, leading to changes in global temperatures and weather patterns. This, in turn, could have devastating effects on ecosystems and human societies.
The consequences of a weakened magnetic field can be far-reaching. Some of the potential effects include:
- Disruption to navigation systems, including GPS and compasses, which rely on the magnetic field for orientation
- Increased radiation exposure for both humans and wildlife, particularly at high altitudes and near the poles
- Changes to the formation of clouds and precipitation patterns, potentially leading to more extreme weather events
- Impacts on the Earth's geology, including the formation of minerals and the movement of tectonic plates
The scientific community is still working to understand the causes and consequences of the weakening magnetic field. Researchers are using a combination of satellite data, ground-based observations, and computer modeling to study the phenomenon. By better understanding the Earth's magnetic field and its role in the planet's systems, scientists hope to predict and prepare for the potential effects of its decline.
In terms of navigation, the weakening magnetic field could have significant implications for industries such as aviation, maritime, and logistics. Pilots and sailors rely on magnetic compasses and GPS systems to navigate, and disruptions to these systems could have serious safety and economic consequences. As the magnetic field continues to weaken, it is essential to develop new technologies and strategies to mitigate these effects and ensure the continued reliability of navigation systems.




