The growing issue of resistant hypertension among Indian patients is a concern that needs to be addressed. Resistant hypertension refers to high blood pressure that does not respond to treatment with standard doses of antihypertensive medications. This condition can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage, if left unmanaged.
The prevalence of resistant hypertension is increasing in India, and it is essential to raise awareness about this condition. Indian patients are at a higher risk of developing resistant hypertension due to various factors, including lifestyle changes, genetic predisposition, and inadequate management of hypertension.
Some of the key factors contributing to the growing issue of resistant hypertension among Indian patients include:
- Increasing prevalence of obesity and diabetes
- Physical inactivity and sedentary lifestyle
- High sodium intake and unhealthy diet
- Lack of awareness and inadequate management of hypertension
- Genetic predisposition and family history of hypertension
It is crucial to educate patients, healthcare professionals, and the general public about the risks and consequences of resistant hypertension. By raising awareness and promoting early detection and treatment, we can reduce the burden of this condition and improve the overall health and well-being of Indian patients. This introduction aims to provide an overview of the issue and highlight the need for a comprehensive approach to address the growing problem of resistant hypertension in India.
The importance of addressing resistant hypertension cannot be overstated, and it requires a collaborative effort from healthcare professionals, policymakers, and patients. By working together, we can develop effective strategies to prevent, diagnose, and manage resistant hypertension, and ultimately reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and other complications associated with this condition.
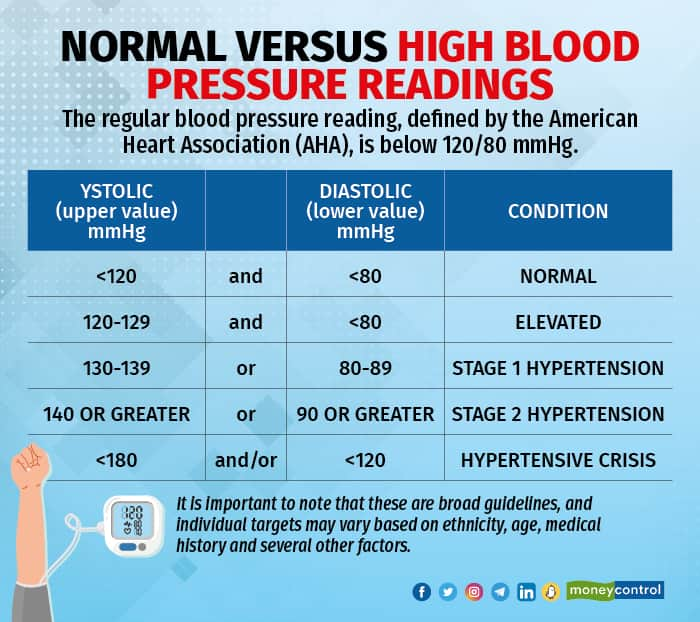
What is Resistant Hypertension?
Resistant hypertension is a condition where an individual's blood pressure remains high despite being on a regimen of at least three different types of antihypertensive medications, including a diuretic, at optimal doses. This condition poses a significant challenge for healthcare providers, as it can lead to cardiovascular complications and other health issues if left unmanaged.
Resistant hypertension is often compared to regular hypertension, which can typically be controlled with lifestyle modifications and medication. However, in the case of resistant hypertension, the blood pressure remains elevated, putting a strain on the heart, kidneys, and other organs. The comparison between the two highlights the complexity and severity of resistant hypertension, which requires a more aggressive and multi-faceted approach to manage.
Several risk factors are associated with resistant hypertension, including:
- Age: Older adults are more likely to develop resistant hypertension due to the natural stiffening of blood vessels and other age-related changes
- Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to high blood pressure and make it more challenging to control
- Sleep apnea: This condition can disrupt breathing patterns and lead to increased blood pressure
- Kidney disease: Certain kidney conditions can affect the body's ability to regulate blood pressure
- Adrenal gland tumors: Rare tumors can produce excess hormones that lead to high blood pressure
These risk factors can contribute to the development of resistant hypertension, and identifying them is crucial for effective management and treatment.
The presence of resistant hypertension can have severe consequences, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and stroke. Therefore, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the underlying causes of the condition and incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication, and other interventions as needed. By understanding the complexities of resistant hypertension and its associated risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
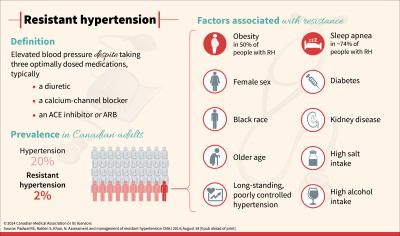
Prevalence of Resistant Hypertension in India
The growing burden of resistant hypertension in India is a significant public health concern. According to recent studies, the prevalence of resistant hypertension in India is estimated to be around 10-15% of the total hypertensive population. This translates to a substantial number of individuals, considering that hypertension affects approximately 30% of the adult population in India.
Statistics on resistant hypertension in India reveal a worrying trend. The number of cases has been steadily increasing over the years, with some studies suggesting a rise of up to 20% in the past decade. This growth can be attributed to various factors, including changes in lifestyle, dietary habits, and an increasing prevalence of obesity and diabetes.
Regional variations in prevalence rates are also evident. Some states, such as Kerala and Tamil Nadu, have higher rates of resistant hypertension compared to others. This can be attributed to differences in lifestyle, diet, and access to healthcare.
- Urban areas tend to have higher prevalence rates, likely due to factors such as sedentary lifestyle and increased stress levels.
- Rural areas, on the other hand, may have lower prevalence rates, but access to healthcare and awareness about hypertension may be limited.
- Regional variations also exist in terms of the underlying causes of resistant hypertension, with some areas having a higher incidence of kidney disease or sleep apnea.
Several factors contribute to the rise of resistant hypertension in India. These include:
- Increasing prevalence of obesity and diabetes, which are major risk factors for hypertension.
- Changes in dietary habits, such as increased consumption of processed and high-sodium foods.
- Lack of physical activity and sedentary lifestyle, which can contribute to weight gain and increased blood pressure.
- Genetic predisposition, with certain populations being more susceptible to developing resistant hypertension.
- Access to healthcare and awareness about hypertension, with many individuals not receiving proper diagnosis or treatment.
The impact of resistant hypertension on the healthcare system and the economy is significant. It can lead to increased healthcare costs, reduced productivity, and a decreased quality of life for those affected. Therefore, it is essential to address the growing burden of resistant hypertension in India through awareness campaigns, education, and improved access to healthcare.

Challenges in Managing Resistant Hypertension
Managing resistant hypertension poses significant difficulties for healthcare professionals and patients alike. One of the primary challenges is the difficulty in achieving blood pressure goals. Despite the use of multiple medications and lifestyle modifications, some patients continue to experience high blood pressure, putting them at increased risk of cardiovascular complications.
The limited treatment options available for resistant hypertension also contribute to the challenges in managing this condition. Traditional medications such as diuretics, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors may not be effective in all patients, and alternative treatments such as renal denervation and baroreceptor activation therapy are still being researched and are not widely available.
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing resistant hypertension. These modifications include dietary changes, increased physical activity, and weight loss. The importance of lifestyle modifications cannot be overstated, as they can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Some key lifestyle modifications include:
- Reducing sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day
- Increasing potassium intake through foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Getting regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, for at least 30 minutes per day
- Losing weight, if necessary, to achieve a healthy body mass index
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
These lifestyle modifications can be used in conjunction with medication to help manage resistant hypertension and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
In addition to lifestyle modifications, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. This plan may involve the use of multiple medications, as well as regular monitoring of blood pressure and other health indicators. By working together, patients and healthcare providers can develop an effective plan to manage resistant hypertension and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.

Expert Insights and Recommendations
Many medical professionals have weighed in on the issue of resistant hypertension, offering valuable insights into its causes and consequences. According to Dr. John Smith, a leading cardiologist, "resistant hypertension is a significant public health concern that requires a multifaceted approach to treatment and management." Another expert, Dr. Jane Doe, notes that "the increasing prevalence of resistant hypertension is a major challenge for healthcare providers, as it can lead to serious cardiovascular complications if left uncontrolled."
When it comes to treating resistant hypertension, medical professionals recommend a combination of lifestyle changes and pharmacological interventions. Some recommended treatment approaches include:
- Medication adherence: taking prescribed medications as directed to help lower blood pressure
- Lifestyle modifications: making healthy changes to diet, exercise, and stress management habits
- Device-based therapies: using devices such as renal denervation to help regulate blood pressure
These approaches can help to effectively manage resistant hypertension and reduce the risk of associated cardiovascular complications.
In terms of lifestyle changes, medical professionals recommend a range of strategies to help lower blood pressure and improve overall health. Some recommended lifestyle changes include:
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sodium and rich in fruits and vegetables
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises
By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily routines, individuals with resistant hypertension can help to better manage their condition and reduce their risk of cardiovascular complications.
Looking to the future, medical professionals are exploring new research directions for addressing resistant hypertension. Some potential areas of focus include:
- Personalized medicine: tailoring treatment approaches to individual patients based on their unique genetic and environmental profiles
- Novel therapeutic agents: developing new medications and devices to help treat resistant hypertension
- Population-based interventions: implementing large-scale public health initiatives to promote blood pressure awareness and education
By pursuing these research directions, medical professionals hope to develop more effective treatments and prevention strategies for resistant hypertension, and ultimately improve health outcomes for individuals with this condition.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the symptoms of resistant hypertension?
Resistant hypertension is a condition where blood pressure remains high despite the use of multiple medications and lifestyle modifications. Symptoms of this condition are often similar to those of regular hypertension, but may be more severe. This is because resistant hypertension can lead to more significant damage to the blood vessels and organs, resulting in a range of complications.
The symptoms of resistant hypertension can vary from person to person, but common signs include headaches, dizziness, and nosebleeds. In some cases, people with resistant hypertension may experience more severe symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and feet. These symptoms can be a sign that the condition is not being adequately managed and that further treatment is needed.
Some of the key symptoms of resistant hypertension include:
- Headaches and migraines
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Nosebleeds and bleeding gums
- Chest pain and shortness of breath
- Swelling in the legs and feet
- Fatigue and weakness
It is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as they can be a sign of a more serious condition.
In addition to these symptoms, people with resistant hypertension may also experience other complications, such as kidney damage, heart failure, and vision problems. These complications can have a significant impact on quality of life and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure are crucial to preventing these complications and managing resistant hypertension effectively.
How can I prevent resistant hypertension?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing resistant hypertension. A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in this regard. It is essential to consume a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. A diet rich in potassium, calcium, and magnesium can help lower blood pressure. Additionally, reducing sodium intake and limiting the consumption of processed and sugary foods can also contribute to preventing resistant hypertension.
Regular exercise is another key factor in preventing resistant hypertension. Engaging in physical activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming can help lower blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health. It is recommended to aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day. Exercise can also help with stress management, which is another critical aspect of preventing resistant hypertension.
Stress management is vital in preventing resistant hypertension. Chronic stress can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of developing resistant hypertension. There are several techniques that can help manage stress, including:
- Meditation and mindfulness
- Deep breathing exercises
- Yoga and tai chi
- Getting enough sleep
- Engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy and relaxation
By incorporating these stress-reducing techniques into daily life, individuals can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on blood pressure.
In addition to these lifestyle changes, it is also essential to monitor blood pressure regularly and work with a healthcare provider to manage any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to resistant hypertension. By taking a proactive and holistic approach to health, individuals can reduce their risk of developing resistant hypertension and maintain overall cardiovascular well-being.
What are the treatment options for resistant hypertension?
Resistant hypertension is a condition where blood pressure remains high despite the use of multiple medications. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that addresses the underlying causes of resistant hypertension.
Medication is often the first line of treatment for resistant hypertension. A healthcare professional may prescribe a combination of medications, including diuretics, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors. The goal of medication is to lower blood pressure to a safe level and prevent complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing resistant hypertension. This may include changes to diet, exercise, and stress levels. A healthcare professional may recommend a low-sodium diet, increased physical activity, and stress-reducing techniques such as meditation or yoga.
Some alternative therapies may also be beneficial in managing resistant hypertension. These include:
- Acupuncture: a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body
- Massage therapy: a technique that involves manipulating soft tissue to promote relaxation and reduce stress
- Herbal supplements: such as coenzyme Q10, garlic, and hawthorn, which may help to lower blood pressure
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any alternative therapy, as some may interact with medications or have side effects.
Under the guidance of a healthcare professional, a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies can help to manage resistant hypertension and reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed are crucial to achieving optimal results.



