The United States has long been a key player in Middle Eastern politics, and in recent years, the Trump administration has taken a keen interest in resolving the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. In 2020, the Trump administration unveiled a peace plan for the Gaza Strip, which was shared at the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) with various Islamic nations, including Pakistan. This move was seen as a significant development in the region's complex geopolitics.
The context of the peace plan is rooted in the decades-long conflict between Israel and Palestine, with the Gaza Strip being a major point of contention. The plan aimed to address the economic and humanitarian challenges faced by the people of Gaza, while also promoting regional stability and security. By sharing the plan with Islamic nations, including Pakistan, the Trump administration sought to garner support and build a coalition to help implement the plan.
The purpose of the peace plan was multifaceted, with key objectives including:
- Promoting economic growth and development in the Gaza Strip
- Improving the humanitarian situation in the region
- Enhancing regional security and stability
- Fostering cooperation and dialogue between Israel and Palestine
- Encouraging international support and investment in the peace process
By achieving these objectives, the Trump administration hoped to create a more peaceful and prosperous environment in the Gaza Strip, which would have far-reaching benefits for the entire region.
The involvement of Islamic nations, including Pakistan, was crucial to the success of the peace plan. These countries have significant influence in the region and could play a key role in promoting the plan and encouraging other nations to support it. By engaging with Islamic nations, the Trump administration aimed to build a broad coalition to help drive the peace process forward and create a more stable and secure Middle East.

Background of the Gaza Peace Plan
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has a long and complex historical context, dating back to the early 20th century. The conflict began as a dispute over land and has since evolved into a multifaceted issue, involving politics, religion, and national identity. The creation of the State of Israel in 1948 led to the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, known as the Nakba or "catastrophe" in Arabic, which has been a major point of contention ever since.
The search for a peaceful resolution to the conflict has been ongoing for decades, with numerous plans and initiatives proposed over the years. Previous peace plans, such as the Oslo Accords in 1993 and the Kerry Initiative in 2013, have aimed to establish a two-state solution, with Israel and Palestine coexisting as separate entities. However, these plans have ultimately failed to achieve lasting peace, due to a range of factors, including disagreements over borders, settlements, and security arrangements.
Some notable previous peace plans include:
- The Camp David Summit in 2000, which aimed to establish a framework for a comprehensive peace agreement
- The Arab Peace Initiative in 2002, which proposed a regional approach to resolving the conflict
- The Annapolis Conference in 2007, which sought to revive negotiations and achieve a two-state solution
These plans have had varying degrees of success, but ultimately, a lasting resolution to the conflict has yet to be achieved.
In 2020, the Trump administration unveiled a new peace plan, which included a range of key components, such as:
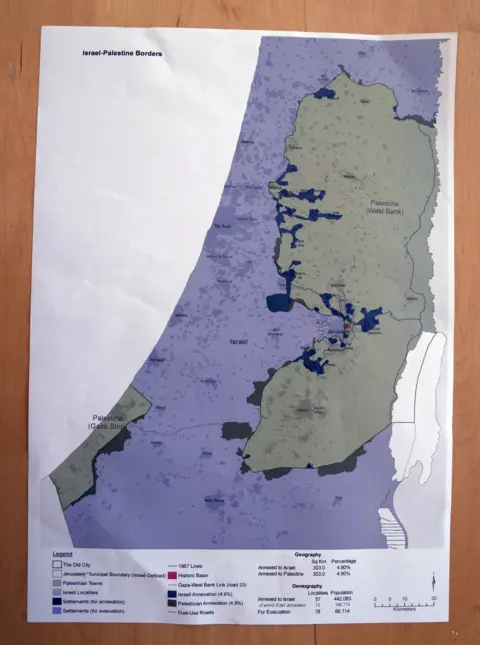
- A proposed map for a future Palestinian state, which would include parts of the West Bank and Gaza
- A plan for Israel to annex certain areas of the West Bank, including settlements and the Jordan Valley
- A proposal for a $50 billion investment in the Palestinian economy, aimed at promoting economic development and stability
The plan was met with widespread criticism from Palestinians and many in the international community, who argued that it was biased towards Israel and failed to address key issues, such as the right of return for Palestinian refugees and the status of Jerusalem.

Key Components of Trump's Gaza Peace Plan
Border adjustments and territorial swaps are crucial aspects of the plan. The proposal involves altering the current borders to create a more contiguous and viable Palestinian state. This would be achieved through a series of territorial swaps, where Israel would relinquish control of certain areas in exchange for others. The goal is to minimize the displacement of people and ensure that the new borders are secure and mutually beneficial.
The plan also addresses Jerusalem's status and the management of religious sites. The city's future is a highly contentious issue, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming it as their capital. The proposal suggests a creative solution, where Jerusalem would be divided into separate zones, each governed by a different authority. This would allow for the protection of holy sites and ensure that all parties have access to their revered places of worship.
Economic development and investment in Gaza are essential for the long-term success of the plan. The proposal includes provisions for significant investment in Gaza's infrastructure, including the construction of new roads, bridges, and utilities. This would help to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and improve living standards. Some of the key economic initiatives include:
- Establishing a free trade zone to encourage entrepreneurship and foreign investment
- Developing the tourism sector, with a focus on Gaza's rich history and cultural heritage
- Improving access to education and vocational training, to equip Gazans with the skills needed to compete in the global economy
- Enhancing the private sector, through support for small and medium-sized enterprises and start-ups
These economic initiatives would be supported by a comprehensive investment plan, which would provide funding for key projects and initiatives. The goal is to create a thriving economy in Gaza, one that is integrated into the regional and global economy, and provides opportunities for all Gazans to prosper. By addressing the economic, territorial, and religious aspects of the conflict, the plan aims to create a lasting and comprehensive peace in the region.
Reaction from Pakistan and Other Islamic Nations
Official statements from Pakistan have been cautious, with the government calling for a peaceful resolution to the conflict. The Pakistani foreign ministry has issued statements emphasizing the need for a negotiated settlement that takes into account the concerns of all parties involved. Other key Islamic countries, such as Turkey and Iran, have also issued statements calling for peace and stability in the region.
In terms of official responses, the following countries have made notable statements:
- Iran: Called for a peaceful resolution and expressed support for a negotiated settlement.
- Turkey: Emphasized the need for a diplomatic solution and offered to facilitate talks between the parties involved.
- Indonesia: Expressed concern over the humanitarian situation and called for an end to violence.
- Malaysia: Urged all parties to exercise restraint and work towards a peaceful resolution.
The potential implications for regional politics and diplomacy are significant. The responses from Pakistan and other Islamic nations could influence the trajectory of the conflict and impact the prospects for a peaceful resolution. A unified stance from Islamic countries could put pressure on other nations to support a negotiated settlement, while divisions among these countries could hinder progress towards peace.
In comparison with previous international responses to peace plans, the current reaction from Pakistan and other Islamic nations is notable for its caution and emphasis on diplomacy. Previous responses have often been more divisive, with some countries supporting one side or the other. The current approach, which emphasizes the need for a negotiated settlement and peaceful resolution, may be more conducive to achieving a lasting peace.
The implications of these responses will depend on how they are received by other nations and the parties involved in the conflict. If the international community can present a united front in support of a peaceful resolution, it may be possible to achieve a breakthrough in the conflict. However, if divisions emerge among Islamic countries or between these countries and other nations, it could hinder progress towards peace and exacerbate the conflict.

Implementation Challenges and Future Prospects
The success of any plan relies heavily on the political will and cooperation needed from all parties involved. This means that governments, organizations, and individuals must work together towards a common goal. Without this cooperation, the plan is likely to face significant challenges and may ultimately fail.
One of the key aspects of political will is the commitment to provide the necessary resources and support for the plan. This includes financial resources, expertise, and infrastructure. The international community can play a crucial role in supporting the plan by providing these resources and helping to build capacity.
The role of the international community in supporting the plan cannot be overstated. The international community can provide financial and technical assistance, as well as share best practices and expertise. This can help to build capacity and ensure that the plan is implemented effectively. Some of the ways the international community can support the plan include:
- Providing financial assistance to help implement the plan
- Sharing best practices and expertise to help build capacity
- Providing technical assistance to help overcome obstacles
Despite the potential benefits of the plan, there are also potential obstacles and criticisms that must be considered. Some of the potential obstacles include:
- Lack of political will and cooperation from all parties
- Insufficient resources and support
- Conflict and instability in the region
These obstacles can be significant and may require careful planning and management to overcome. The plan must also be flexible and adaptable to respond to changing circumstances and criticisms.
Criticisms of the plan may include concerns about the potential impact on certain groups or communities, as well as the potential for unintended consequences. These criticisms must be carefully considered and addressed in order to ensure that the plan is effective and sustainable. By working together and addressing these challenges, it is possible to overcome the obstacles and ensure the success of the plan.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the main differences between Trump's plan and previous peace proposals?
Trump's plan marks a significant shift in the approach to Middle East peace negotiations. One of the primary differences between this plan and previous proposals is the level of detail and specificity. Earlier initiatives, such as the Oslo Accords and the Clinton Parameters, focused on broad principles and frameworks for peace. In contrast, Trump's plan provides a detailed map for a two-state solution, including borders, security arrangements, and economic development.
The plan also deviates from earlier initiatives in its approach to Jerusalem. Previous proposals had suggested a divided city, with Israel and Palestine exercising sovereignty over different areas. Trump's plan, on the other hand, recognizes Jerusalem as Israel's capital and allows for the possibility of Palestinian sovereignty over certain neighborhoods. This approach has been met with significant criticism from Palestinian leaders and other stakeholders.
Some key features of Trump's plan that distinguish it from earlier initiatives include:
- A detailed map for a two-state solution, including borders and security arrangements
- Recognition of Jerusalem as Israel's capital, with possible Palestinian sovereignty over certain neighborhoods
- A focus on economic development and investment in the Palestinian territories
- A phased approach to Palestinian statehood, with certain conditions and milestones that must be met before full sovereignty is achieved
Trump's plan builds upon earlier initiatives in its emphasis on economic development and cooperation. The plan proposes a significant investment in the Palestinian economy, with the goal of creating jobs and improving living standards. This approach is similar to earlier initiatives, such as the Oslo Accords, which also emphasized the importance of economic cooperation and development.
The plan's focus on security is also reminiscent of earlier initiatives, such as the Clinton Parameters. However, Trump's plan takes a more detailed and prescriptive approach, outlining specific security arrangements and protocols for the Palestinian territories. This approach has been met with criticism from some stakeholders, who argue that it does not provide sufficient flexibility or autonomy for Palestinian security forces.
How does the plan address the status of Jerusalem, a critical issue for both Israelis and Palestinians?
The status of Jerusalem is a highly contentious issue, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming the city as their capital. Any plan attempting to resolve the Israeli-Palestinian conflict must address this critical issue. The plan proposes a compromise on Jerusalem's governance, aiming to satisfy the concerns of both parties.
The plan suggests dividing Jerusalem into two capitals, with the Jewish neighborhoods falling under Israeli jurisdiction and the Arab neighborhoods under Palestinian control. This division would allow for the establishment of two separate capitals, while ensuring that the city remains open and accessible to all residents.
Regarding governance, the plan proposes the creation of a joint committee to oversee the management of shared resources and services in Jerusalem. This committee would comprise representatives from both the Israeli and Palestinian governments, as well as international experts. The committee's responsibilities would include managing the city's infrastructure, public services, and environmental issues.
In terms of access to religious sites, the plan guarantees freedom of worship and access to holy sites for all religions. The plan proposes the following provisions:
- Ensuring that the Temple Mount/Haram al-Sharif is accessible to Muslims, Jews, and Christians, with arrangements for joint administration and security
- Guaranteeing the rights of Christians to access and worship at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and other holy sites in Jerusalem
- Establishing a mechanism for resolving disputes and addressing concerns related to access to and management of religious sites
- Encouraging interfaith dialogue and cooperation to promote understanding and respect among the different religious communities in Jerusalem
These provisions aim to balance the competing interests and concerns of the various stakeholders in Jerusalem, ensuring that the city remains a symbol of peace, tolerance, and coexistence. By addressing the status of Jerusalem in a comprehensive and equitable manner, the plan seeks to create a foundation for a lasting and just resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
What role is envisioned for Pakistan and other Islamic nations in supporting the implementation of the peace plan?
The implementation of a peace plan requires a collective effort from nations around the world, including Pakistan and other Islamic nations. These countries can play a vital role in supporting the peace process through various forms of assistance.
Diplomatic support is one of the key areas where Islamic nations can contribute. This can be achieved through high-level diplomatic engagements, mediation efforts, and facilitating dialogue between conflicting parties.
Some potential forms of support that Islamic nations could provide include:
- Hosting peace talks and negotiations between parties involved in the conflict
- Providing mediators or special envoys to facilitate dialogue and negotiation
- Offering diplomatic channels to help resolve disputes and address grievances
Economic support is another crucial aspect of supporting the implementation of a peace plan. Islamic nations can provide financial assistance, humanitarian aid, and economic investments to help rebuild and stabilize affected regions.
In addition to diplomatic and economic support, Islamic nations can also provide other forms of assistance, such as:
- Humanitarian aid, including food, shelter, and medical assistance
- Economic investments in infrastructure development and job creation
- Capacity-building programs to help strengthen institutions and promote good governance
Pakistan, in particular, can play a significant role in supporting the peace process due to its strategic location and historical ties with other Islamic nations. By working together, Islamic nations can help create a more stable and peaceful environment, which is essential for the successful implementation of a peace plan.
The role of Islamic nations in supporting the peace plan is not limited to providing assistance, but also extends to promoting a culture of peace and tolerance. By promoting interfaith dialogue, understanding, and cooperation, Islamic nations can help create an environment that is conducive to peace and stability.
Overall, the support of Islamic nations, including Pakistan, is crucial to the successful implementation of a peace plan. Through diplomatic, economic, and other forms of assistance, these nations can help create a more stable and peaceful environment, which is essential for promoting prosperity and development in the region.




