As we delve into the world of liver diseases, it is essential to understand the prevalence and impact of these conditions in India. The country has seen a significant rise in liver-related disorders, and it is crucial to create awareness about the most common diseases affecting the liver. A gastrointestinal surgeon has shed light on the prevalent liver diseases in India, which will be discussed in this blog post.
The liver plays a vital role in our body, performing various functions such as detoxification, metabolism, and production of essential proteins. Any damage to the liver can lead to severe health complications, making it essential to understand the common liver diseases. According to the gastrointestinal surgeon, some of the most common liver diseases in India include:
- Hepatitis B and C
- Alcoholic Liver Disease
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- Liver Cancer
- Cirrhosis
These liver diseases can be caused by various factors, including viral infections, excessive alcohol consumption, and unhealthy lifestyle choices. The gastrointestinal surgeon emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and treatment to prevent the progression of liver diseases. By understanding the common liver diseases prevalent in India, we can take necessary precautions to prevent these conditions and maintain a healthy liver.
In the following sections, we will discuss each of these liver diseases in detail, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. The information provided is based on the expertise of a gastrointestinal surgeon, ensuring that the readers receive accurate and reliable information about liver diseases. By the end of this blog post, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the common liver diseases in India and the necessary steps to prevent and manage these conditions.

Introduction to Liver Diseases
Liver diseases are a significant concern for public health in India, with a substantial number of people affected every year. The liver is a vital organ that performs various functions, including detoxification, metabolism, and production of essential proteins. Any damage to the liver can lead to severe health complications, making it essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods.
The impact of liver diseases on public health in India is alarming, with liver cancer being one of the most common types of cancer in the country. According to recent statistics, liver diseases account for a significant percentage of hospitalizations and deaths in India. The main causes of liver diseases include viral hepatitis, alcohol consumption, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and genetic disorders.
Awareness and prevention are crucial in reducing the burden of liver diseases. It is essential to educate people about the risk factors, symptoms, and prevention methods to promote early detection and treatment. Some of the ways to prevent liver diseases include:
- Getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Maintaining a healthy weight and diet
- Avoiding sharing personal care items, such as razors and toothbrushes
- Practicing safe sex to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B and C
By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing liver diseases.
The importance of awareness and prevention cannot be overstated, as liver diseases can be asymptomatic in the early stages, making it challenging to detect. If left untreated, liver diseases can lead to severe complications, such as liver failure, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Therefore, it is essential to promote awareness and prevention methods to reduce the burden of liver diseases on public health in India.
Regular health check-ups and screenings can help detect liver diseases early, making it possible to initiate treatment and prevent further complications. By working together, we can reduce the impact of liver diseases on public health in India and promote a healthier future for all.
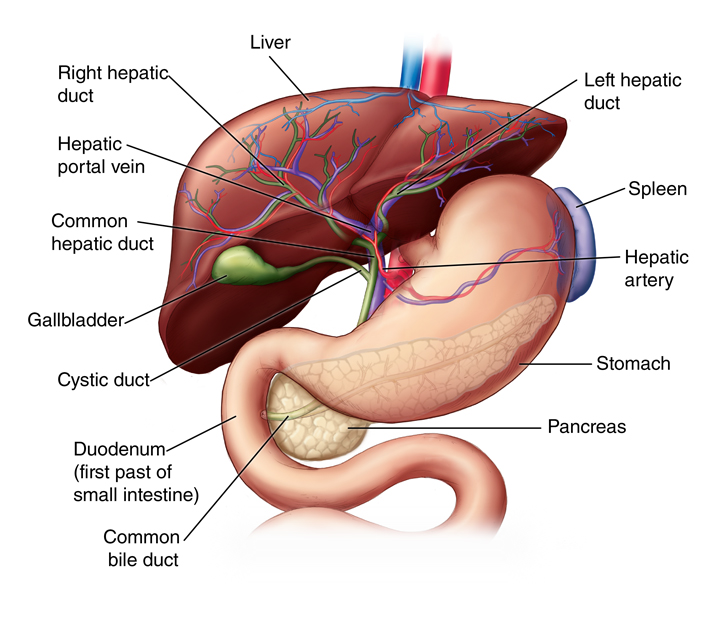
4 Most Common Liver Diseases in India
Fatty liver disease is a common condition in India, where excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. This disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including obesity, diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption. The symptoms of fatty liver disease may not be apparent in the early stages, but as the condition progresses, patients may experience fatigue, weight loss, and abdominal pain. Prevention of fatty liver disease can be achieved through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
The symptoms of fatty liver disease can be managed, and the condition can be prevented by making lifestyle changes. Some of the ways to prevent fatty liver disease include:
- Consuming a balanced diet that is low in saturated fats and high in fiber
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, for at least 30 minutes a day
- Limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels
- Managing stress through techniques such as yoga or meditation
Viral hepatitis is another common liver disease in India, which is caused by a viral infection. There are several types of viral hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, and C. These viruses can be transmitted through contaminated food and water, blood transfusions, and sexual contact. The treatment of viral hepatitis depends on the type and severity of the infection, but it often involves antiviral medications and lifestyle changes.
Liver cirrhosis is a condition where the liver becomes scarred and damaged, often due to years of inflammation and cell death. The stages of liver cirrhosis include:
- Compensated cirrhosis, where the liver is still able to function normally
- Decompensated cirrhosis, where the liver is no longer able to function properly
The complications of liver cirrhosis can be severe and include liver failure, kidney damage, and an increased risk of liver cancer. Management of liver cirrhosis involves treating the underlying cause of the condition, as well as managing the symptoms and complications.
Liver cancer is a serious condition that can be caused by a variety of risk factors, including viral hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and aflatoxin exposure. The diagnosis of liver cancer often involves imaging tests, such as ultrasound and CT scans, as well as blood tests to detect tumor markers. The treatment options for liver cancer depend on the stage and severity of the condition, but they may include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Some of the treatment options for liver cancer include:
- Surgical resection, where the tumor is removed surgically
- Liver transplantation, where the diseased liver is replaced with a healthy one
- Targeted therapy, where medications are used to target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells

Prevention and Management of Liver Diseases
Diet and lifestyle play a crucial role in preventing liver diseases. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy liver. It is essential to limit the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats, as they can contribute to liver damage. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can also help reduce the risk of liver diseases.
A well-planned diet should include foods that support liver health, such as:
- Leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale
- Citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits
- Nuts and seeds like almonds and sunflower seeds
- Fatty fish like salmon and sardines
These foods are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats that can help protect the liver from damage.
Vaccination against hepatitis is also essential in preventing liver diseases. Hepatitis A and B vaccines are available and can provide long-term protection against these viral infections. It is recommended that individuals at high risk of contracting hepatitis, such as healthcare workers and travelers to certain countries, get vaccinated. Vaccination can help prevent the spread of hepatitis and reduce the risk of liver damage.
Screening and early detection of liver diseases are critical in managing and treating these conditions. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify liver problems early on, when they are more treatable. Screening tests may include:
- Liver function tests to check for liver damage
- Imaging tests like ultrasound and CT scans to visualize the liver
- Blood tests to check for viral infections like hepatitis
Early detection and treatment can help prevent liver diseases from progressing to more severe conditions, such as liver failure or liver cancer.
In addition to screening and vaccination, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential in managing liver diseases. This includes avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, not smoking, and getting regular exercise. By combining a healthy diet, regular screening, and a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of developing liver diseases and manage existing conditions effectively.

Expert Insights and Recommendations
Maintaining a healthy liver is crucial for overall well-being, and according to gastrointestinal surgeons, there are several ways to achieve this. A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is essential, as it provides the necessary nutrients for liver function. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is vital for flushing out toxins from the liver.
Regular health check-ups and screenings are also vital for maintaining a healthy liver. These check-ups can help identify any potential issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing further damage. Some of the key health checks to consider include:
- Liver function tests to assess liver damage or disease
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans to visualize the liver
- Screenings for liver cancer and other related diseases
These tests can help identify any underlying issues and provide a clear understanding of liver health.
The latest advancements in liver disease treatment and management have significantly improved patient outcomes. New medications and therapies have been developed to treat various liver conditions, including hepatitis and liver cancer. Furthermore, advancements in surgical techniques have made liver transplants and other procedures safer and more effective. Some of the latest developments in liver disease treatment include:
- Targeted therapies to treat liver cancer and other diseases
- Immunotherapy to boost the body's immune system and fight disease
- Gene therapy to correct genetic disorders affecting the liver
These advancements have revolutionized the field of liver disease treatment and management, offering new hope for patients with liver conditions.
In terms of lifestyle changes, gastrointestinal surgeons recommend avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding exposure to toxins. These simple changes can significantly reduce the risk of liver disease and promote overall liver health. By combining a healthy lifestyle with regular health check-ups and screenings, individuals can take a proactive approach to maintaining a healthy liver and reducing the risk of liver disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the most common symptoms of liver disease?
Liver disease can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms can be subtle, making it challenging to diagnose in the early stages. One of the most common symptoms of liver disease is fatigue. This can be a feeling of general weakness, lack of energy, and a tendency to tire easily. People with liver disease may find it difficult to perform daily tasks and may need to take frequent breaks to rest.
Another noticeable symptom of liver disease is jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes. This occurs when the liver is not able to remove bilirubin, a pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells, from the blood. Jaundice can also cause dark urine and pale stools.
Some common symptoms of liver disease include:
- Abdominal pain, which can be a dull ache or a sharp pain in the upper right side of the abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting, which can lead to weight loss and malnutrition
- Loss of appetite, which can further exacerbate weight loss and fatigue
- Itching, which can be severe and debilitating in some cases
- Dark circles under the eyes, which can be a sign of liver dysfunction
Abdominal pain and swelling are also common symptoms of liver disease. The pain can be caused by the liver becoming enlarged or inflamed, while the swelling can be due to a buildup of fluid in the abdomen. In some cases, liver disease can also cause mental fogginess, mood changes, and personality changes. These symptoms can be distressing and disrupt daily life, making it essential to seek medical attention if they persist or worsen over time.
Early detection and treatment of liver disease can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term damage. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and care. They can perform diagnostic tests, such as blood tests and imaging studies, to determine the underlying cause of the symptoms and develop an effective treatment plan.
Can liver diseases be prevented through diet and lifestyle changes?
A healthy liver is essential for overall well-being, and diet and lifestyle play a significant role in maintaining liver health. A well-balanced diet provides the liver with the necessary nutrients to function properly, while a poor diet can lead to liver damage and disease. Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support liver health.
Regular exercise is also crucial for maintaining a healthy liver. Exercise helps to improve blood flow and boost the immune system, which can help to prevent liver disease. Additionally, exercise can help with weight management, which is important for reducing the risk of fatty liver disease.
Some key dietary and lifestyle changes that can help prevent liver diseases include:
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in saturated and trans fats
- Avoiding excessive sugar and salt consumption
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Limiting intake of processed and packaged foods
- Getting enough sleep and managing stress
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is also essential for preventing liver disease. Alcohol is a major risk factor for liver disease, and excessive drinking can lead to liver damage and scarring. Limiting alcohol intake or avoiding it altogether can help to reduce the risk of liver disease. By making these simple dietary and lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing liver disease and maintain overall health and well-being.
How often should I get screened for liver diseases?
Liver disease screening is an essential step in detecting and managing liver conditions, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. The frequency of screening depends on various factors, including individual risk factors and medical history. Generally, people with a higher risk of developing liver disease should undergo more frequent screenings.
Individuals with a family history of liver disease, those who are overweight or obese, and people with a history of heavy alcohol consumption are at a higher risk of developing liver disease. Additionally, people with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, should also be screened more frequently.
The following groups of people should undergo liver disease screening:
- People with a family history of liver disease, especially those with a first-degree relative who has been diagnosed with liver disease
- Individuals who are overweight or obese, as excess weight can increase the risk of developing liver disease
- People with a history of heavy alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol use can damage the liver
- Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol
The recommended frequency of liver disease screening varies depending on individual risk factors and medical history. For people with a high risk of liver disease, screening should be done every 6-12 months. For those with a moderate risk, screening should be done every 1-2 years. People with a low risk of liver disease may only need to undergo screening every 2-3 years.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the recommended frequency of liver disease screening based on individual risk factors and medical history. A healthcare provider can assess the risk of liver disease and recommend the best course of action for screening and prevention. Regular screening can help detect liver disease early, when it is more treatable, and prevent long-term damage to the liver.




