Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing this condition from progressing and causing permanent damage. The introduction to this topic serves as a foundation for understanding the significance of timely intervention.
The primary goal of early diagnosis is to identify the signs and symptoms of diabetic retinopathy before they become severe. This can be achieved through regular eye exams and screenings, which enable healthcare professionals to detect any abnormalities in the blood vessels of the retina. By catching the condition early, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent further complications.
Some of the key benefits of early diagnosis and treatment include:
- Prevention of vision loss: Early treatment can help prevent vision loss by stopping the progression of the disease.
- Reduced risk of complications: Timely intervention can reduce the risk of complications, such as blindness and eye damage.
- Improved quality of life: By preventing vision loss, individuals with diabetes can maintain their independence and quality of life.
Regular monitoring and treatment can also help individuals with diabetes to better manage their condition and reduce the risk of related complications. This highlights the importance of education and awareness about diabetic retinopathy, as well as the need for individuals with diabetes to take an active role in their eye health. By prioritizing early diagnosis and treatment, individuals with diabetes can protect their vision and maintain their overall health.

What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that affects people with diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This damage can cause the blood vessels to leak, swell, or even grow abnormally, leading to vision problems and potentially blindness.
The connection to diabetes is clear: people with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy due to the high levels of glucose in their blood. Over time, this excess glucose can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, leading to the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy. The risk of developing this condition increases with the duration of diabetes, as well as the level of blood sugar control.
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina in several ways. The main causes of damage include:
- Weakening of blood vessel walls, making them more prone to leakage
- Blockage of blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the retina
- Growth of new, fragile blood vessels that can easily bleed
- Inflammation and scarring of the retina, leading to vision loss
These changes can occur gradually over many years, making it essential for people with diabetes to have regular eye exams to monitor their eye health.
Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can help prevent vision loss and slow the progression of the disease. By managing blood sugar levels, getting regular eye exams, and seeking prompt treatment for any vision problems, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing this serious eye condition. Regular monitoring and timely intervention can make a significant difference in preserving vision and maintaining overall eye health.

Symptoms and Detection
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. The symptoms of this condition can be subtle at first, but they can worsen over time if not addressed. One of the most common symptoms of diabetic retinopathy is blurred vision. This can occur when the blood vessels in the retina become damaged, causing them to leak or bleed.
Floaters are another common symptom of diabetic retinopathy. These are small spots that appear to float in front of the eyes, and they can be caused by the formation of scar tissue or the presence of blood in the vitreous gel. In some cases, diabetic retinopathy can also cause blind spots or vision loss, especially if the macula is affected.
The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy can vary from person to person, but some common signs include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Floaters or flashes of light
- Dark spots or blind spots
- Pain or pressure in the eyes
- Double vision
Regular eye exams are essential for early detection of diabetic retinopathy. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes have a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year. During this exam, the doctor will use specialized equipment to examine the retina and detect any signs of damage. Early detection is crucial, as it can help prevent vision loss and blindness.
Early detection and treatment of diabetic retinopathy can significantly improve outcomes. With proper care, it is possible to slow or even halt the progression of the disease. This is why regular eye exams are so important for people with diabetes. By catching the condition early, it is possible to prevent serious complications and protect vision.

Stages and Treatment Options
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can cause blindness if left untreated. The disease progresses through several stages, each with distinct symptoms and treatment options. The stages of diabetic retinopathy are classified based on the severity of the damage to the blood vessels in the retina.
The early stages of diabetic retinopathy are often mild and may not exhibit noticeable symptoms. As the disease progresses, it can cause significant damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems. The stages of diabetic retinopathy include mild non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, moderate non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
The treatment options for diabetic retinopathy depend on the stage and severity of the disease. Some of the treatment options include:
- Medications to reduce swelling and prevent further vision loss
- Laser surgery to destroy abnormal blood vessels and reduce swelling
- Vitrectomy, a surgical procedure to remove blood and scar tissue from the eye
- Intraocular injections of medications to reduce swelling and prevent further vision loss
Laser surgery is often used to treat proliferative diabetic retinopathy, while vitrectomy is typically reserved for advanced cases where there is significant bleeding or scarring in the eye.
In addition to these treatment options, lifestyle changes such as controlling blood sugar levels, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly can also help to slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Regular eye exams are also crucial for detecting the disease early and preventing vision loss. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the outcome for individuals with diabetic retinopathy, and can help to preserve vision and prevent blindness.
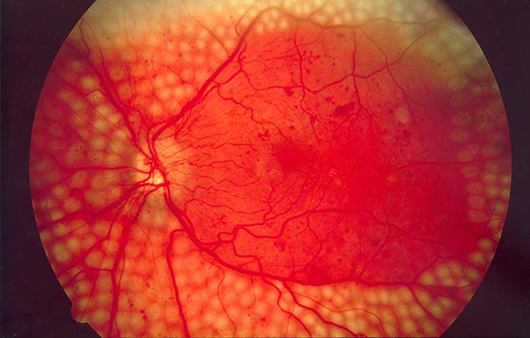
Prevention and Management
Proper diabetes management plays a crucial role in preventing diabetic retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness. By controlling blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of developing this condition. Effective management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical treatments, which can help to prevent or delay the onset of diabetic retinopathy.
Maintaining healthy vision is essential for individuals with diabetes, and a balanced diet is a key component of this. Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help to promote overall health and reduce the risk of complications. Regular exercise is also important, as it can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
Some tips for maintaining healthy vision include:
- Eating a balanced diet that includes foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts
- Getting regular eye exams to detect any potential problems early
- Quitting smoking, as smoking can increase the risk of diabetic retinopathy
- Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as high levels can increase the risk of complications
In addition to these tips, it is also important for individuals with diabetes to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, and to avoid foods that are high in sugar and salt. By making these lifestyle modifications and working with a healthcare provider to manage their diabetes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy and promote overall health and well-being. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and adjustment of treatment plans as needed can also help to prevent complications and promote healthy vision.
%2520(2)%2520(1).jpeg)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the risk factors for developing diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to blindness if left untreated. The development of diabetic retinopathy is influenced by several key factors.
One of the primary risk factors is the duration of diabetes. The longer a person has diabetes, the higher their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. This is because prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina over time.
High blood sugar levels are another significant risk factor for diabetic retinopathy. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to the development of diabetic retinopathy.
Some other risk factors for diabetic retinopathy include:
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can further damage the blood vessels in the retina, increasing the risk of diabetic retinopathy
- Pregnancy: Women with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing diabetic retinopathy during pregnancy
- Genetics: A family history of diabetic retinopathy can increase a person's risk of developing the condition
It is essential for people with diabetes to manage their condition effectively to reduce their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. This includes maintaining good blood sugar control, attending regular eye exams, and managing other health conditions, such as hypertension. By taking these steps, individuals with diabetes can help protect their vision and reduce their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Can diabetic retinopathy be reversed?
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing them to swell and leak. In some cases, new blood vessels may grow, but they are often weak and prone to bleeding.
Early detection is crucial in preventing vision loss. Regular eye exams can help identify the condition in its early stages, allowing for prompt treatment. Treatment options may include laser therapy, injections, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. While some damage can be reversed with treatment, the key to minimizing vision loss is early detection and prevention.
Some of the ways to prevent or slow down the progression of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Managing blood sugar levels through a healthy diet and regular exercise
- Controlling high blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke
- Getting regular eye exams to monitor the condition
By taking these steps, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing diabetic retinopathy and minimize the risk of vision loss.
In addition to these preventive measures, researchers are also exploring new treatments for diabetic retinopathy. These include new medications and therapies that aim to reverse or slow down the progression of the condition. While these treatments hold promise, early detection and prevention remain the most effective ways to minimize vision loss.
It is essential for individuals with diabetes to take an active role in managing their condition and preventing complications like diabetic retinopathy. By working closely with their healthcare team and taking steps to manage their blood sugar levels and overall health, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of vision loss and maintain their eye health.
How often should diabetics get their eyes checked?
People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing eye problems, such as diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma. Regular eye exams are crucial to detect these conditions early and prevent vision loss. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes get a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year.
This recommendation applies to people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, as well as those with gestational diabetes. Even if a person's blood sugar levels are under control, they should still get their eyes checked annually. The eye exam should include a thorough evaluation of the retina, macula, and optic nerve.
Some individuals may need to get their eyes checked more frequently, such as:
- Those with a history of eye problems or vision loss
- Pregnant women with diabetes, who should get an eye exam in the first trimester and possibly more often if recommended by their doctor
- People with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, who may need to get their eyes checked every 6 months
During a comprehensive eye exam, the doctor will check for signs of diabetic retinopathy, such as bleeding or swelling in the retina. They will also check for cataracts, glaucoma, and other eye conditions that can affect people with diabetes. By getting regular eye exams, people with diabetes can help protect their vision and prevent long-term damage to their eyes.
In addition to annual eye exams, people with diabetes should also be aware of the warning signs of eye problems, such as blurred vision, double vision, or eye pain. If they experience any of these symptoms, they should contact their doctor right away. By taking proactive steps to protect their eye health, people with diabetes can reduce their risk of vision loss and maintain their overall health and well-being.




%2520(2)%2520(1).jpeg)