As the world's fastest-growing major economy, India has been navigating a complex landscape of growth, inflation, and fiscal reforms. In recent years, the country has made significant strides in liberalizing its economy, attracting foreign investment, and implementing policies aimed at promoting economic inclusion. However, the Indian economy has also faced its fair share of challenges, including a slowing growth rate, rising unemployment, and a widening fiscal deficit.
The Current Economic Climate
Today, India's economy is at a critical juncture. The COVID-19 pandemic has dealt a severe blow to the country's growth momentum, with the GDP growth rate slowing down to 4.2% in 2020-21. The pandemic has not only disrupted supply chains and impacted consumer demand but also exacerbated existing structural issues, such as a struggling agriculture sector, a precarious banking system, and a volatile currency market. Furthermore, the ongoing global trade tensions and geopolitical uncertainties have added to the economic uncertainty, making it challenging for policymakers to chart a course for sustained growth. Goods and Services Levy (GST) - A Game-Changer in Indian Economy In this context, the Goods and Services Levy (GST), introduced in 2017, has been a significant reform aimed at simplifying the indirect tax regime and promoting economic growth. GST has replaced multiple indirect taxes, including excise duty, service tax, and value-added tax (VAT), with a single, unified tax rate. This has helped to create a seamless national market, reduce tax evasion, and increase tax compliance.Modi's Announcement on Reducing GST - A Boost to Economic Growth
Against this backdrop, Prime Minister Narendra Modi's recent announcement on reducing the GST rate has sent ripples of excitement across the economy. The move is expected to provide a much-needed stimulus to the economy, particularly to the struggling small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and the retail sector. By reducing the GST burden, the government aims to increase consumer demand, boost economic activity, and create jobs.- The GST rate reduction is expected to benefit a wide range of industries, including textiles, gemstones, and jewellery, which are significant contributors to India's exports and employment.
- The move is also likely to benefit the common man, as it will lead to a decrease in the prices of essential commodities and services.
- Moreover, the GST rate reduction is expected to increase tax compliance, as businesses will be incentivized to pay taxes and claim input credits, thereby reducing the scope for tax evasion.

The Current State of India's Economy
The Current Economic Situation
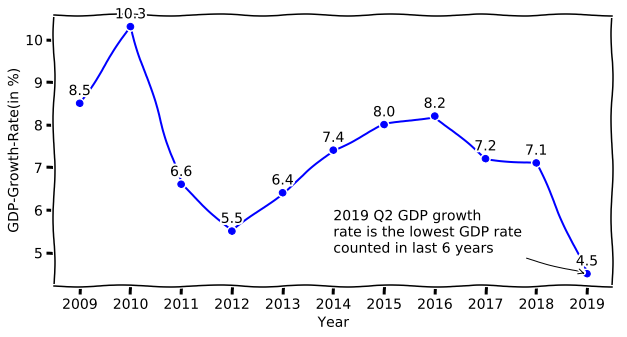
India's economy has been growing at a rate of around 7% per annum, which is relatively slow compared to its potential. The country's GDP growth rate has been declining over the past few years, from 8.2% in 2016-17 to 5.3% in 2020-21. The slowdown can be attributed to various factors, including:- Weakened consumer demand, particularly in the rural areas
- Decline in investment and savings rates
- Slow pace of economic reforms
- Global economic uncertainty
Challenges Faced by the Economy
India's economy is facing several challenges that need to be addressed to achieve sustainable growth. Some of the key challenges include:- High unemployment rates: India's unemployment rate has been increasing, particularly among the youth. This can lead to social unrest and negatively impact consumer demand.
- Inflationary pressures: The country has been witnessing high inflation rates, particularly in food and fuel prices. This can reduce consumer purchasing power and affect economic growth.
- Fiscal constraints: The government's fiscal deficit has been increasing, which can limit its ability to invest in key areas such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare.
- Dependence on imports: India's economy is heavily dependent on imports, particularly in the energy sector. This can make it vulnerable to global economic shocks.
Importance of Economic Reforms
To overcome the challenges faced by the economy and achieve sustainable growth, it is essential to implement economic reforms. Some of the key reforms that can help stimulate economic growth include:- Labour market reforms: Simplifying labour laws and increasing the ease of doing business can attract investments and create jobs.
- Privatization of state-owned enterprises: Privatizing state-owned enterprises can increase efficiency and attract investments.
- Tax reforms: Implementing a simplified and competitive tax regime can increase tax compliance and attract investments.
- Investment in infrastructure: Investing in infrastructure, including roads, ports, and energy, can increase the country's competitiveness and attract investments.
Modi's Plan to Cut Goods and Services Levy
The Current Challenges
Despite its benefits, the current GST structure has faced criticism for being complex and having multiple tax rates. The 28% tax slab, in particular, has been a subject of debate, with many arguing that it is too high and has led to higher prices for consumers. Additionally, the GST system has been plagued by issues such as delayed refunds, complicated compliance procedures, and the burden of multiple tax rates.The Proposed Changes
In response to these challenges, the Indian government, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has proposed significant changes to the GST system. The main objective of these changes is to simplify the tax structure, reduce the burden on consumers, and increase revenue for the government. The proposed changes include:- Rationalization of tax rates: The government plans to reduce the number of tax rates and simplify the tax structure. This could involve merging the 12% and 18% tax slabs into a single rate, and reducing the 28% tax slab.
- Lowering of tax rates: The government is considering reducing the tax rates on certain goods and services, such as food items, textiles, and construction materials.
- Simplification of compliance procedures: The government aims to simplify the GST compliance procedures, reduce the frequency of tax filings, and make it easier for businesses to claim refunds.
- Expansion of the tax base: The government plans to expand the GST tax base by bringing more goods and services under the tax net, and increasing the tax compliance rate.
Benefits of the Reduced Levy
The proposed changes to the GST system are expected to have several benefits for consumers, businesses, and the economy as a whole. Some of the benefits of the reduced levy include:- Lower prices for consumers: The reduction in tax rates will lead to lower prices for consumers, making goods and services more affordable.
- Boost to economic growth: The simplified tax structure and lower tax rates will encourage economic growth, increase demand, and lead to job creation.
- Increased tax compliance: The simplified compliance procedures and lower tax rates will increase tax compliance, leading to higher revenue for the government.
- Competitiveness: The reduced levy will make Indian goods and services more competitive in the global market, leading to an increase in exports.

Impact of the Reforms on Indian Businesses and Consumers
The Reduced GST: A Boon for Indian Businesses
The recent reforms in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime have brought about a significant reduction in tax rates for various goods and services. This move is expected to have a profound impact on Indian businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The reduced GST rates will provide a much-needed respite to businesses that were struggling to cope with the high tax burden. One of the primary benefits of the reduced GST is the increased competitiveness of Indian businesses in the global market. With lower tax rates, businesses will be able to offer their products and services at competitive prices, making them more attractive to customers. This, in turn, will help businesses to increase their market share and expand their customer base.- Increased Profit Margins: The reduced GST rates will result in higher profit margins for businesses, as they will no longer have to bear the burden of high tax rates. This will enable them to invest in new technologies, expand their operations, and create new job opportunities.
- Improved Cash Flow: The reduced GST rates will also improve the cash flow of businesses, as they will have to pay less tax. This will enable them to meet their working capital requirements and invest in new projects.
- Simplified Compliance: The reduced GST rates will also simplify compliance for businesses, as they will no longer have to deal with multiple tax rates and complex tax laws.
Benefits for Consumers
The reduced GST rates will not only benefit businesses but also consumers. With lower tax rates, consumers will have to pay less for goods and services, which will increase their purchasing power. This, in turn, will boost demand and stimulate economic growth.- Increased Affordability: The reduced GST rates will make goods and services more affordable for consumers, particularly those from low-income households. This will improve their standard of living and enable them to access basic necessities.
- Increased Savings: The reduced GST rates will also result in increased savings for consumers, as they will have to pay less tax. This will enable them to invest in other essential goods and services.
- Improved Consumer Experience: The reduced GST rates will also improve the overall consumer experience, as businesses will be able to offer better quality products and services at competitive prices.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
While the reduced GST rates are expected to bring about several benefits for businesses and consumers, there are also some potential challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.- Revenue Loss: The reduced GST rates will result in a revenue loss for the government, which could impact its ability to fund public welfare schemes and infrastructure projects.
- Complexity in Implementation: The implementation of the reduced GST rates may be complex, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may not have the necessary resources and expertise.
- Inequitable Distribution of Benefits: The benefits of the reduced GST rates may not be equitably distributed, with some businesses and consumers benefiting more than others.

Global Implications of India's Economic Reforms
Impact on Global Economy
India's economic reforms are expected to have a profound impact on the global economy. With a growing middle class and an increasing demand for goods and services, India is poised to become a significant driver of global growth. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), India's growth rate is expected to reach 7.3% in 2023, outpacing other major economies. The reforms have also led to an increase in India's competitiveness, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment. This, in turn, has the potential to create new opportunities for trade and investment, driving growth and job creation globally.- The reforms have also led to an increase in India's competitiveness, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment.
- This, in turn, has the potential to create new opportunities for trade and investment, driving growth and job creation globally.
Potential Trade Implications
India's economic reforms have significant trade implications with other countries. The country's growing economy and increasing demand for goods and services create new opportunities for trade and investment. However, the reforms also pose challenges for countries that have traditionally been major trading partners.- The reforms have led to a reduction in tariffs and other trade barriers, making it easier for Indian companies to export goods and services.
- This has the potential to increase competition for companies in other countries, particularly in industries such as textiles and pharmaceuticals.
- On the other hand, the reforms also create new opportunities for countries that can provide goods and services that meet India's growing demand.
Opportunities for Foreign Investment
India's economic reforms have created a favorable business environment, making it an attractive destination for foreign investment. The country's large and growing market, combined with its skilled workforce and competitive costs, make it an ideal location for companies looking to invest in Asia.- The Indian government has introduced a range of incentives and policies to attract foreign investment, including tax breaks and simplified regulations.
- Sectors such as information technology, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy are particularly attractive for foreign investment.
- Companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, and General Electric have already made significant investments in India, and many more are expected to follow.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the current GST rate in India and how will it change?
Understanding the Current GST Rate in India
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive indirect tax system implemented in India on July 1, 2017. The current GST rate in India is a multi-tiered structure, with different rates applicable to different goods and services. The GST Council, comprising the Union Finance Minister, Union Minister of State for Revenue, and State Finance Ministers, determines the GST rates. The current GST rates in India are:- : 0% GST applicable on essential goods like food grains, healthcare services, and educational services.
- : Applicable on precious stones, diamonds, and semi-precious stones.
- : Applicable on gold, silver, and other precious metals.
- : Applicable on common man's goods like coffee, tea, and spices.
- : Applicable on goods like computers, laptops, and certain electrical appliances.
- : Applicable on most goods and services, including FMCG products, electronics, and transportation services.
- : Applicable on luxury goods like automobiles, air travel, and high-end electronics.
Proposed Changes to the GST Rate in India
The GST Council has been reviewing the GST rates regularly to ensure a more efficient and equitable tax system. Some of the proposed changes to the GST rate in India include:- : The GST Council has proposed to reduce the number of GST rates from five to three – 0%, 12%, and 18%. This move aims to simplify the tax system and reduce compliance burden on businesses.
- : The GST Council has proposed to bring petroleum products like petrol, diesel, and natural gas under the GST ambit. This move is expected to reduce the cascading effect of taxes and bring down fuel prices.
- : The GST Council has proposed to review the exemptions granted to certain goods and services, including exemptions on healthcare and educational services. This move aims to broaden the tax base and increase revenue collections.
How will the reduction in GST affect the prices of essential goods?
The reduction in Goods and Services Tax (GST) has been a welcome move for many consumers, but the question on everyone's mind is: how will it impact the prices of essential goods like food and medicine? In this section, we'll delve into the details of the GST reduction and its effects on the prices of these essential items. Understanding the GST Reduction Before we dive into the impact of the GST reduction on essential goods, it's essential to understand the recent changes made to the tax structure. The GST Council, the apex body responsible for deciding GST rates, has reduced the tax rates on various items, including food and medicine. The reduction in GST rates is expected to make these essential goods more affordable for consumers. Impact on Food Prices The reduction in GST rates on food items is expected to have a significant impact on their prices. With the new GST rates, many food items, including:
- Rice, wheat, and other cereals
- Pulses, flour, and other staple food items
- Spices, including turmeric, coriander, and cumin
- Tea, coffee, and other beverages
- Life-saving drugs, including those for cancer, HIV, and diabetes
- Medicines for chronic diseases, such as hypertension and asthma
- Vaccines and other medical devices
- Increase in Purchasing Power: With lower prices, consumers will have more purchasing power, enabling them to afford more goods and services.
- Relief for Low-Income Households: The reduction in GST rates will provide relief to low-income households, who spend a significant portion of their income on essential goods like food and medicine.
- Boost to Economic Growth: The reduction in GST rates is expected to boost economic growth by increasing demand, which will, in turn, lead to an increase in production and employment.
What are the potential challenges and limitations of Modi's economic reforms?
Challenges in Implementation
While Modi's economic reforms aim to revitalize India's economy, their implementation is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is the complexity of the reforms, which can lead to confusion and misinterpretation among stakeholders. For instance, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) reform, although well-intentioned, has been criticized for its complex nature, leading to difficulties in compliance and implementation. Another significant challenge is the resistance to change among certain sections of society. The reforms often require a shift in mindset and business practices, which can be daunting for some individuals and organizations. This resistance can manifest in various forms, including protests, strikes, and even violence, thereby hindering the implementation of reforms.Institutional Limitations
India's institutional framework also poses significant challenges to the effective implementation of economic reforms. The bureaucratic red tape and corruption can slow down the process, making it difficult to achieve the desired outcomes. Additionally, the judicial system's slow pace can lead to delays in resolving disputes, thereby affecting the overall progress of reforms. Moreover, the limited capacity of government agencies can hinder the effective implementation of reforms. Many government agencies lack the necessary resources, including trained personnel, infrastructure, and technology, to efficiently implement and monitor the reforms.Funding and Resource Constraints
The implementation of economic reforms also requires significant funding and resources. However, India faces fiscal constraints, which can limit the government's ability to invest in key areas such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare. This can, in turn, affect the overall impact of the reforms. Furthermore, the dependence on external funding can also pose a challenge. India's economy is heavily dependent on foreign investment, which can be volatile and susceptible to global economic trends. This can lead to uncertainty and affect the country's ability to implement reforms effectively.Social and Environmental Concerns
Modi's economic reforms have also been criticized for their potential social and environmental implications. The displacement of marginalized communities, particularly in the context of land acquisition for infrastructure projects, is a significant concern. Similarly, the environmental degradation resulting from rapid industrialization and infrastructure development can have long-term consequences for the country's ecosystem. In conclusion, while Modi's economic reforms have the potential to transform India's economy, their implementation is not without its challenges and limitations. Addressing these concerns will be crucial to ensuring the success of the reforms and achieving sustainable economic growth.-
Key Takeaways:
- The complexity of reforms can lead to confusion and misinterpretation.
- Resistance to change can hinder the implementation of reforms.
- Institutional limitations, such as bureaucratic red tape and corruption, can slow down the process.
- Funding and resource constraints can limit the government's ability to invest in key areas.
- Social and environmental concerns, such as displacement and environmental degradation, need to be addressed.

