The Indian economy has witnessed a significant overhaul in recent times, with the introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017. This radical tax reform aimed to simplify the complex tax structure, promote ease of doing business, and create a unified national market. However, the GST rates have undergone several changes since its inception, and the recent revisions have sparked intense debate among economists, policymakers, and consumers alike. Understanding the Implications The latest GST rate revisions have far-reaching implications for both the Indian economy and its consumers. It is essential to comprehend the effects of these changes to navigate the evolving business landscape and make informed decisions. Economic Implications
- Inflationary Pressures: The revised GST rates are expected to influence the overall inflation rate in the country. A hike in GST rates can lead to increased production costs, which may be passed on to consumers, resulting in higher prices and inflation.
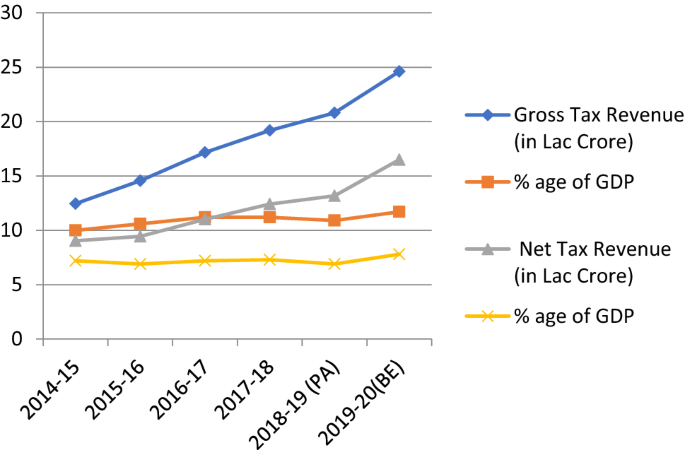
- Revenue Generation: The GST rate revisions can significantly impact the government's revenue collection. Higher GST rates can lead to increased revenue, while lower rates may result in reduced revenue generation.
- Industry-Specific Impact: The revised GST rates will have varying effects on different industries. For instance, a rate hike on luxury goods may benefit the economy, while a rate cut on essential items may boost consumer demand.
- Pocket Impact: The revised GST rates will directly affect the purchasing power of consumers. A hike in GST rates can reduce consumer spending, while a rate cut can increase disposable income.
- Price Volatility: The changes in GST rates can lead to price fluctuations, making it challenging for consumers to budget and plan their expenses.
- Changing Consumption Patterns: The revised GST rates may influence consumer behavior, with some opting for cheaper alternatives or reducing their consumption of luxury goods.
What is GST 2.0 and its Key Features
- Simplified Return Filing: GST 2.0 introduces a simplified return filing system, reducing the number of returns to be filed by taxpayers from 37 to just 12.
- Single GST Rate: The new regime proposes a single GST rate for each commodity, eliminating the complexity of multiple rates.
- Taxpayers' Convenience: GST 2.0 provides an enhanced taxpayer interface, enabling easy tracking of returns, payments, and refunds.
- Improved Compliance: The new regime introduces a system of automated return filing, reducing the scope for errors and increasing compliance.
- Reduced Tax Rates: GST 2.0 proposes reduced tax rates for certain goods and services, providing relief to taxpayers and consumers.
- Streamlined Refund Process: The revamped regime introduces a faster and more efficient refund process, reducing the time taken for refunds to be processed.
- Reduced Tax Burden: The two-slab system reduces the tax burden on essential goods and services, making them more affordable for consumers.
- Incentivizing Economic Growth: The lower tax rate for essential goods and services encourages economic growth, as it increases demand and promotes consumption.
- Discouraging Consumption of Demerit Goods: The higher tax rate for luxury and demerit goods discourages their consumption, promoting a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle.
- Increased Revenue: The two-slab system is expected to increase revenue for the government, as it widens the tax base and reduces tax evasion.

Goods and Services That Get Cheaper
- Sanitary Napkins: GST rate reduced from 12% to 0%
- Rakhis: GST rate reduced from 10% to 0%
- Furniture: GST rate reduced from 28% to 18%
- Televisions up to 32 inches: GST rate reduced from 28% to 18%
- Refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners: GST rate reduced from 28% to 18%
- Hotel rooms with tariffs up to ₹7,500: GST rate reduced from 28% to 18%
- Outdoor catering services: GST rate reduced from 18% to 5%
- Movie tickets: GST rate reduced from 28% to 18%

Goods and Services That Get Costlier
- Mobile phones and specified parts: The GST rate on mobile phones and specified parts will increase from 12% to 18%. This means that mobile phone prices will rise, making them more expensive for consumers.
- Televisions and monitors: The GST rate on televisions and monitors with screen sizes above 32 inches will increase from 18% to 28%. This will result in higher prices for these electronic devices.
- Footwear and furniture: The GST rate on footwear with a retail price of over ₹1,000 and furniture will increase from 18% to 28%. This will lead to higher prices for these consumer goods.
- Cosmetics and skincare products: The GST rate on certain cosmetics and skincare products will increase from 18% to 28%. This will result in higher prices for these personal care products.
- Hotel rooms with a tariff above ₹7,500: The GST rate on hotel rooms with a tariff above ₹7,500 will increase from 18% to 28%. This will result in higher room rates for luxury hotels.
- Railway catering services: The GST rate on railway catering services will increase from 5% to 12%. This will lead to higher prices for food and beverages on trains.

Impact on Indian Economy and Consumers
- Reduced Prices: The reduction in tax rates on various goods and services will lead to a decrease in prices, making them more affordable for consumers.
- Increased Transparency: The new tax regime provides for a transparent tax structure, enabling consumers to know the exact amount of tax they are paying.
- Improved Compliance: GST 2.0 is expected to improve tax compliance, reducing the incidence of tax evasion and ensuring that consumers are not cheated by unscrupulous businesses.
- Wider Reach: The new tax regime is expected to increase the reach of goods and services, particularly in rural areas, providing consumers with greater access to goods and services.
- Increased Prices of Luxury Goods: The increase in tax rates on luxury goods such as cars, air travel, and hospitality services will lead to an increase in prices, making them less affordable for consumers.
- Complexity: The new tax regime is still complex, with multiple tax rates and slabs, which can cause confusion among consumers.
- Higher Burden on Small Businesses: GST 2.0 may increase the compliance burden on small businesses, which may pass on the costs to consumers.
- Job Losses: The new tax regime may lead to job losses in certain industries, particularly those that are heavily reliant on exemptions and concessions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When will the new GST rates come into effect?
As the Indian government continues to refine and improve the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, taxpayers and businesses are eagerly awaiting the implementation of GST 2.0. The new GST rates are expected to bring about significant changes to the existing tax structure, simplifying compliance and reducing complexities. The Union Budget 2023-24 has announced the implementation of GST 2.0, which is expected to come into effect from October 1, 2023. This new regime aims to address the existing challenges and anomalies in the GST system, providing a more streamlined and efficient tax environment for businesses and consumers alike. Key Features of GST 2.0 ---------------------
- Simplified Tax Rates: GST 2.0 is expected to introduce a simplified tax rate structure, reducing the number of tax slabs from five to three. This will lead to a more uniform and predictable tax environment, making it easier for businesses to comply with GST regulations.
- Removal of Inverted Duty Structure: The new GST regime will eliminate the inverted duty structure, which currently leads to refund-related issues and input tax credit (ITC) complexities. This change will benefit industries such as textiles, fertilizers, and pharma, among others.
- Enhanced Compliance Mechanism: GST 2.0 will introduce an enhanced compliance mechanism, featuring a more robust and technology-driven system to monitor and track GST compliance. This will help reduce tax evasion and improve revenue collection.
- Streamlined Refund Process: The new regime will introduce a more streamlined refund process, reducing the processing time and making it easier for businesses to claim refunds.
- Reviewing and updating their accounting and compliance systems to align with the new GST regime.
- Assessing the impact of the new tax rates and structures on their business operations and pricing strategies.
- Developing strategies to optimize their GST compliance and minimize potential disruptions.
Will GST 2.0 lead to a reduction in prices of all goods and services?
The introduction of GST 2.0 has sparked a wave of optimism among consumers, with many hoping that it will lead to a reduction in prices of goods and services. While the reduction in GST rates is a welcome move, it's essential to understand that it may not necessarily translate to a decrease in prices. In this article, we'll delve into the reasons why GST rate reduction may not lead to a reduction in prices. GST Rate Reduction: A Complex Affair GST rate reduction is a complex process that involves multiple stakeholders, including manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers. While a reduction in GST rates may provide some relief to consumers, it's not always a straightforward process. Manufacturers and suppliers may not pass on the benefits of GST rate reduction to consumers, and here's why. Anti-Profiteering Measures One of the primary reasons GST rate reduction may not lead to a reduction in prices is the lack of effective anti-profiteering measures. Anti-profiteering measures are designed to ensure that businesses pass on the benefits of GST rate reduction to consumers. However, in the absence of robust measures, businesses may not reduce prices, despite the reduction in GST rates. Input Tax Credit Another reason GST rate reduction may not lead to a reduction in prices is the concept of input tax credit. Under GST, businesses can claim input tax credit on the GST paid on inputs. However, if the GST rate on inputs is reduced, businesses may not pass on the benefits to consumers, as they can still claim input tax credit at the higher rate. Cost of Compliance GST compliance requires significant investments in technology, infrastructure, and manpower. Businesses may factor in these costs while pricing their products, which could offset the benefits of GST rate reduction. Therefore, even if GST rates are reduced, prices may not decrease due to the increased cost of compliance. Profit Margins Businesses operate on profit margins, and GST rate reduction may not necessarily lead to a reduction in prices if businesses choose to maintain their profit margins. For instance, if a business is selling a product at ₹100 with a profit margin of 20%, it may not reduce the price even if the GST rate is reduced, as it can still maintain its profit margin. Other Factors Influencing Prices GST rate reduction is just one of the many factors that influence prices. Other factors, such as:
- Raw material costs
- Labour costs
- Transportation costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Seasonal demand
How will GST 2.0 impact small businesses and startups?
The introduction of GST 2.0 is expected to bring about significant changes in the tax landscape of India, and small businesses and startups are likely to be impacted the most. While GST 2.0 aims to simplify the tax compliance process and reduce tax rates, its implications on small businesses and startups are still unclear. Compliance Burden One of the major concerns for small businesses and startups is the compliance burden under GST 2.0. With the new system, businesses will be required to file multiple returns, including GSTR-1, GSTR-2, and GSTR-3, which can be a daunting task, especially for small businesses with limited resources. Additionally, the requirement to maintain detailed records and invoices will add to the compliance burden. Tax Burden The tax burden on small businesses and startups is also expected to increase under GST 2.0. While the tax rates have been reduced, the threshold for GST registration has been increased from Rs. 20 lakh to Rs. 40 lakh, which means that more businesses will be required to register for GST. This will lead to an increase in tax liability for many small businesses and startups. Impact on Cash Flow GST 2.0 is also expected to impact the cash flow of small businesses and startups. With the requirement to pay taxes on a monthly basis, businesses will need to ensure that they have sufficient liquidity to meet their tax obligations. This can be a challenge for small businesses and startups that often struggle with cash flow management. Benefits of GST 2.0 Despite the challenges, GST 2.0 is expected to bring some benefits for small businesses and startups. For instance, the new system will allow for input tax credit, which will help reduce the tax burden on businesses. Additionally, the simplified tax compliance process will reduce the need for multiple registrations and filings, making it easier for businesses to operate. Key Implications Some of the key implications of GST 2.0 on small businesses and startups include:
- Increase in compliance burden: Small businesses and startups will need to invest time and resources in maintaining detailed records and filing multiple returns.
- Increase in tax burden: The increase in threshold for GST registration will lead to an increase in tax liability for many small businesses and startups.
- Cash flow management: Businesses will need to ensure that they have sufficient liquidity to meet their tax obligations on a monthly basis.
- Benefits of input tax credit: The new system will allow for input tax credit, which will help reduce the tax burden on businesses.
- Simplified tax compliance process: The new system will reduce the need for multiple registrations and filings, making it easier for businesses to operate.

