The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine has been a subject of great concern for the international community, with the European Union playing a crucial role in attempting to resolve the crisis. To understand the current state of affairs, it's essential to delve into the historical context that has led to the escalating tensions between these two nations. The Post-Soviet Era Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Ukraine gained independence, and Russia emerged as a dominant power in the region. The two countries have since had a complex relationship, with Ukraine seeking to assert its sovereignty and Russia attempting to maintain its influence over its former Soviet republics. The Orange Revolution In 2004, Ukraine's Orange Revolution saw the country shift towards a more pro-European stance, with President Viktor Yushchenko seeking to integrate Ukraine into the European community. This move was met with resistance from Russia, which viewed Ukraine's drift towards the West as a threat to its interests. The Annexation of Crimea In 2014, Russia annexed Crimea, a peninsula in Ukraine with significant strategic importance. This move was widely condemned by the international community, and it marked a turning point in the conflict between Russia and Ukraine. The Conflict in Eastern Ukraine Following the annexation of Crimea, pro-Russian separatists in eastern Ukraine declared independence, leading to a conflict that has resulted in thousands of deaths and the displacement of millions of people. Russia has been accused of providing military support to the separatists, a claim it has consistently denied. The European Union's Response The European Union has been at the forefront of international efforts to resolve the conflict, imposing sanctions on Russia in response to its actions in Ukraine. The EU has also provided significant financial assistance to Ukraine, aimed at supporting the country's economic development and promoting democratic reforms.
- In 2014, the EU imposed economic sanctions on Russia, targeting its financial, energy, and defense sectors.
- In 2015, the EU and Ukraine signed an Association Agreement, which aimed to deepen economic and political ties between the two parties.
- In 2019, the EU extended its sanctions on Russia, citing a lack of progress in resolving the conflict in eastern Ukraine.

The EU's Proposal: Deploying Troops to Ukraine
- Providing security and protection to civilians in conflict-affected areas
- Supporting the Ukrainian government in its efforts to restore order and stability
- Monitoring and verifying the ceasefire agreement between Ukraine and Russian-backed separatists
- Facilitating humanitarian assistance and aid delivery to affected populations
- Increasing its military presence along the Ukrainian border
- Providing additional support to Russian-backed separatists in eastern Ukraine
- Imposing economic sanctions on EU member states participating in the deployment
- Engaging in a propaganda campaign to discredit the EU's actions and undermine its credibility

Russia's Rejection: A Hardline Stance on Ukraine
- Fear of NATO Expansion: Russia has long been wary of NATO's expansion into Eastern Europe, and the deployment of EU troops in Ukraine would be seen as a significant step towards further encroachment.
- Protection of Russian Interests: Russia has significant economic and strategic interests in Ukraine, including the crucial port city of Sevastopol, which is home to Russia's Black Sea Fleet.
- Preservation of Regional Influence: By rejecting the EU troop deployment, Russia is seeking to maintain its influence in the region and prevent the EU and NATO from gaining a foothold in Ukraine.
- Escalating Tensions: The move is likely to escalate tensions between Russia and the West, potentially leading to further economic sanctions and diplomatic isolation.
- Increased Instability: Russia's stance may embolden separatist groups in eastern Ukraine, leading to increased violence and instability in the region.
- Diminished Prospects for Peace: The rejection of the EU troop deployment reduces the prospects for a peaceful resolution to the Ukraine crisis, as Russia's hardline stance makes it increasingly difficult to find a compromise.
Zelenskyy's Plea: A Speedy Meeting to Resolve the Crisis
- A unified EU stance on the crisis, with a clear condemnation of Russian aggression and a commitment to supporting Ukraine's sovereignty.
- A package of economic sanctions against Russia, designed to pressure the Kremlin into de-escalating the situation.
- A joint EU-Ukraine statement outlining a roadmap for resolving the conflict, including potential diplomatic talks and confidence-building measures.
- A commitment from EU leaders to provide Ukraine with military aid and support, should the situation deteriorate further.
- Internationalize the crisis, making it clear to Russia that the EU stands firmly behind Ukraine.
- Apply pressure on Russia to de-escalate, by threatening economic sanctions and diplomatic isolation.
- Secure a stronger commitment from the EU to support Ukraine's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Gain a moral and symbolic victory, demonstrating that Ukraine is not alone in its struggle against Russian aggression.

Global Implications: The Broader Ramifications of the Crisis
- The crisis has led to a deterioration in relations between Russia and the West, with the United States, European Union, and other Western nations imposing economic sanctions on Russia.
- The conflict has also strained relations between Russia and its neighbors, such as Poland and the Baltic states, which are increasingly reliant on NATO for their security.
- Furthermore, the crisis has created an opportunity for China to expand its influence in the region, as it seeks to capitalize on the divisions between Russia and the West.
- The crisis has led to a decline in global energy prices, as Russia is a major oil and gas producer.
- The conflict has also disrupted global supply chains, particularly in the aerospace and defense sectors, where Ukraine is a significant player.
- Furthermore, the crisis has led to increased volatility in global financial markets, as investors become increasingly risk-averse.
- The US has been a key player in the crisis, providing military aid to Ukraine and imposing economic sanctions on Russia.
- The European Union has also played a significant role, providing diplomatic and economic support to Ukraine.
- NATO has increased its military presence in Eastern Europe, in response to Russia's actions in Ukraine.
- The conflict has the potential to draw in other regional actors, such as Belarus and Moldova.
- Furthermore, the crisis has the potential to escalate into a wider conflict, involving NATO and other international actors.
- The conflict also has the potential to lead to a new Cold War, with Russia and the West engaged in a prolonged period of geopolitical rivalry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main reason behind Russia's rejection of EU troops in Ukraine?
Russia's reluctance to accept EU troops in Ukraine stems from deep-seated concerns about the EU's military presence in the region and its perceived threat to national security. At the heart of this issue lies a complex web of historical, political, and strategic factors that have contributed to Russia's rejection of EU troops in Ukraine. Historical Context Russia's concerns about EU military presence in Ukraine are rooted in its historical experiences. The country has long been wary of Western military expansion in Eastern Europe, particularly in the aftermath of the Cold War. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) eastward expansion in the 1990s and 2000s has been viewed by Russia as a threat to its national security and a breach of the post-Cold War settlement. National Security Concerns Russia's primary concern is the potential threat that EU troops in Ukraine pose to its national security. Moscow believes that the presence of EU troops would create a hostile military presence on its borders, undermining its ability to defend its territorial integrity. Russia's fear is that EU troops would be used to support Ukraine's integration into NATO, which would further encircle Russia and compromise its national security. Perceived Threat to Regional Stability Russia is also concerned about the potential destabilizing effects of EU troops in Ukraine. Moscow believes that the presence of foreign troops would exacerbate the ongoing conflict in eastern Ukraine, rather than resolving it. Russia argues that the conflict is a domestic issue that should be resolved through political dialogue and negotiations, rather than through the deployment of foreign troops. Concerns about EU's Neocolonialism Russia has also accused the EU of pursuing a neocolonial agenda in Ukraine, seeking to exert its influence over the country's political and economic affairs. Moscow believes that the EU's push for Ukraine's integration into its economic and political structures is a form of economic imperialism, aimed at exploiting Ukraine's resources and undermining Russia's influence in the region. Alternative Solutions Russia has proposed alternative solutions to the conflict in eastern Ukraine, including the deployment of a UN peacekeeping mission and the establishment of a contact group comprising representatives from Ukraine, Russia, and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). Moscow believes that these solutions would be more effective in resolving the conflict and promoting regional stability. In conclusion, Russia's rejection of EU troops in Ukraine is driven by a complex set of historical, political, and strategic factors. Moscow's concerns about the EU's military presence in Ukraine are rooted in its fears about national security, regional stability, and the perceived threat of neocolonialism. To resolve the conflict in eastern Ukraine, Russia believes that alternative solutions must be explored, ones that prioritize dialogue, diplomacy, and regional cooperation over military intervention.
- Russia's historical experiences have contributed to its wariness of Western military expansion in Eastern Europe.
- The presence of EU troops in Ukraine would be seen as a threat to Russia's national security and a breach of the post-Cold War settlement.
- Russia believes that EU troops would exacerbate the conflict in eastern Ukraine, rather than resolving it.
- Moscow has accused the EU of pursuing a neocolonial agenda in Ukraine, seeking to exert its influence over the country's political and economic affairs.
- Russia has proposed alternative solutions to the conflict, including the deployment of a UN peacekeeping mission and the establishment of a contact group comprising representatives from Ukraine, Russia, and the OSCE.
What is the significance of Zelenskyy's meeting with EU leaders in resolving the crisis?
The recent meeting between Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and European Union (EU) leaders marks a significant turning point in the ongoing crisis between Russia and Ukraine. This high-level gathering holds immense potential in facilitating a diplomatic solution and easing tensions between the two nations. Diplomatic Breakthrough The meeting presents an opportunity for EU leaders to mediate a peaceful resolution to the crisis. By engaging in direct talks with Zelenskyy, EU leaders can help broker a deal that addresses the concerns of both Russia and Ukraine. This could involve discussions on key issues such as border control, trade, and energy security. A diplomatic breakthrough would not only alleviate the humanitarian crisis but also prevent further escalation of violence. Easing Tensions The meeting's success in easing tensions between Russia and Ukraine cannot be overstated. A reduction in tensions would have a ripple effect on the entire region, leading to increased stability and security. This, in turn, would enable Ukraine to focus on rebuilding its economy and infrastructure, while also allowing Russia to redirect its resources towards more pressing domestic issues. Key Outcomes The meeting is expected to yield several key outcomes, including:
- Ceasefire Agreement: A commitment from both sides to implement an immediate ceasefire, paving the way for a more permanent solution.
- Humanitarian Aid: An agreement to provide urgent humanitarian assistance to affected regions, including food, medicine, and shelter.
- Diplomatic Channels: The establishment of regular diplomatic channels between Russia and Ukraine, ensuring continuous communication and dialogue.
- Economic Cooperation: A framework for economic cooperation, including trade agreements and energy partnerships, to promote mutual benefit and understanding.
How might the Russia-Ukraine crisis affect global trade and economy?
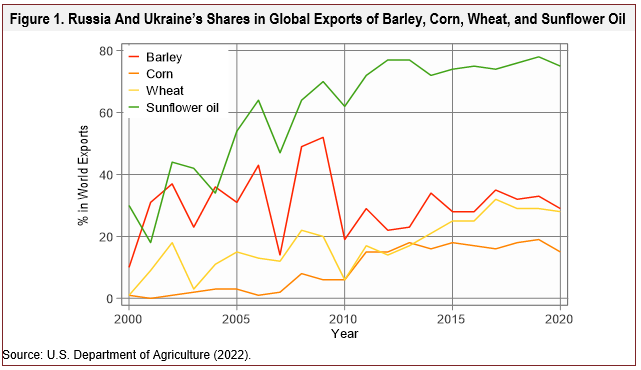
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine crisis has sent shockwaves throughout the global economy, and its impact on international trade is a significant concern. The crisis has the potential to disrupt global supply chains, impose trade sanctions, and create economic instability, ultimately affecting businesses and consumers worldwide. Disruption to Global Supply Chains The Russia-Ukraine conflict is strategically located, with both countries being important players in global trade. Ukraine is a significant producer of agricultural products, such as wheat, corn, and sunflower oil, while Russia is a major exporter of energy resources, including natural gas and oil. Any disruption to their production and export capabilities could have far-reaching consequences for global supply chains.
- Food security concerns: A shortage of Ukrainian agricultural products could lead to food security concerns, particularly in the Middle East and Africa, which rely heavily on Ukrainian exports.
- Energy crisis: Disruptions to Russian energy exports could lead to price volatility, impacting energy-dependent industries and consumers worldwide.
- Manufacturing delays: Supply chain disruptions could lead to delays in manufacturing, particularly in industries that rely on components and raw materials from Russia and Ukraine.
- Economic isolation: Sanctions could isolate Russia from the global economy, limiting its access to international markets and financial systems.
- Trade restrictions: Sanctions could restrict trade between Russia and other countries, impacting exports and imports of goods and services.
- Secondary sanctions: Sanctions could also be imposed on countries that continue to trade with Russia, creating a ripple effect throughout the global economy.
- Market volatility: The crisis has led to market volatility, with stock markets and currencies experiencing significant fluctuations.
- Investment uncertainty: The crisis has created uncertainty for investors, making it challenging to make informed investment decisions.
- Global economic slowdown: Prolonged economic instability could lead to a global economic slowdown, impacting businesses and consumers worldwide.
Promoted
Massive ROI on Your Career: Resume Bundle for Only ₹99
A winning resume is worth thousands in salary. Our bundle of 4,400+ templates costs just ₹99. The ROI is massive.
🔥 Get Lifetime Access Now 🔥
