Glanders, a zoonotic disease, has been a significant concern for animal and human health globally. The disease, caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei, affects equines, primarily horses, donkeys, and mules, and can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated materials. In recent years, the disease has seen a resurgence, highlighting the need for a comprehensive and coordinated approach to control and eliminate it. In response to this growing concern, the Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025 has been launched. This plan is a critical step forward in the fight against Glanders, outlining a roadmap for its control and eventual elimination. The revised plan builds upon the previous national action plan, incorporating lessons learned and best practices from global efforts to combat the disease. The significance of the Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025 lies in its comprehensive and multi-faceted approach. The plan acknowledges that controlling Glanders requires a collaborative effort from various stakeholders, including government agencies, animal health experts, veterinarians, farmers, and the general public. It outlines key strategies and interventions to:
- Enhance surveillance and detection of Glanders cases, enabling early identification and response to outbreaks.
- Strengthen vaccination and immunization programs for equines, reducing the risk of disease transmission.
- Implement biosecurity measures, such as improved hygiene and sanitation practices, to prevent the spread of the disease.
- Foster international collaboration and knowledge sharing, leveraging global expertise and resources to combat Glanders.
- Support research and development of new diagnostic tools, vaccines, and treatments to stay ahead of the evolving disease landscape.
- Raise awareness and education among stakeholders, promoting a culture of responsibility and proactive disease management.
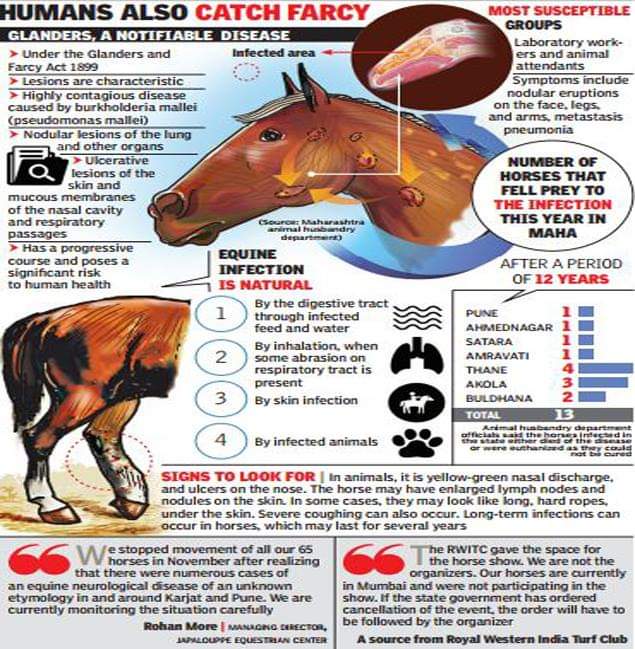
What is Glanders and Why is it a Concern?
- Ulcerative lesions on the skin and mucous membranes
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Respiratory distress
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Ulcerative lesions on the skin and mucous membranes
- Pneumonia
- Meningitis
- Reduced productivity and fertility in infected animals
- Increased mortality rates
- Trade restrictions and embargoes on affected countries
- Loss of livelihoods for those dependent on the equine industry
- Increased healthcare costs
- Lost productivity due to illness
- Impact on tourism and travel industries
- Enhance surveillance and detection of Glanders cases
- Improve diagnostic capabilities and laboratory infrastructure
- Strengthen animal health infrastructure and capacity building
- Implement control measures, such as vaccination and quarantine
- Raise awareness among animal owners, veterinarians, and the general public

Key Objectives of the Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025
- Other key stakeholders that need to be involved in the implementation of the revised plan include state animal husbandry departments, veterinary institutions, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
- The plan recommends the establishment of a National Glanders Task Force to oversee the implementation of the revised plan and ensure coordination among stakeholders.

Implementation and Monitoring of the Revised National Action Plan
- Developing and disseminating guidelines and protocols for the implementation of the plan
- Providing training and capacity-building programs for veterinarians and farmers
- Coordinating and facilitating the sharing of information and resources among stakeholders
- Conducting regular monitoring and evaluation of the plan's progress
- Providing technical assistance and guidance to farmers on animal health and welfare
- Conducting regular monitoring and surveillance of animal diseases
- Reporting and responding to disease outbreaks in a timely and effective manner
- Collaborating with government agencies and farmers to develop and implement disease control and prevention strategies
- Implementing animal health and welfare practices on their farms
- Collaborating with veterinarians and government agencies to develop and implement disease control and prevention strategies
- Providing feedback and input on the effectiveness of the plan
- Adopting and implementing new technologies and practices to improve animal health and welfare
- Clear indicators and targets for measuring progress
- Regular data collection and analysis
- Timely reporting and feedback to stakeholders
- Independent evaluation and review of the plan's effectiveness
- Improving diagnostic tools and techniques for animal diseases
- Developing new and effective vaccines and treatments for animal diseases
- Enhancing animal health and welfare practices and standards
- Investigating and addressing emerging animal disease threats

Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing the Revised National Action Plan
- Knowledge sharing and capacity building
- Joint research and development initiatives
- Technology transfer and adaptation
- Coordinated policy and regulatory frameworks
- International funding agencies and institutions
- Public-private partnerships
- Development banks and financial institutions
- Global donor communities

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the symptoms of Glanders in animals?
Glanders is a highly infectious and debilitating bacterial disease that affects animals, primarily horses, donkeys, and mules. The disease is caused by the bacterium Burkholderia mallei, which is usually transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated fomites. The symptoms of Glanders in animals can vary depending on the route of infection and the severity of the disease. Here are some of the common symptoms of Glanders in animals: Skin Lesions One of the most distinctive symptoms of Glanders is the development of skin lesions, which can appear as nodules, ulcers, or abscesses. These lesions typically occur on the legs, face, and neck of infected animals and can be painful and swollen. In severe cases, the lesions can ulcerate and discharge a thick, yellowish pus. Pneumonia Glanders can also cause respiratory symptoms, particularly pneumonia. Infected animals may exhibit signs of respiratory distress, such as coughing, difficulty breathing, and rapid breathing rate. In severe cases, pneumonia can lead to respiratory failure and death. Lymph Node Enlargement Enlargement of lymph nodes is another common symptom of Glanders in animals. The lymph nodes, particularly those in the neck and shoulder region, may become swollen and painful to the touch. This can be a significant indicator of the disease, as it is often one of the first symptoms to appear. Other Symptoms In addition to skin lesions, pneumonia, and lymph node enlargement, Glanders can cause a range of other symptoms in animals, including:
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Depression
- Lethargy
- Swollen joints
- Abnormal nasal discharge
How can Glanders be prevented and controlled?
Glanders, a highly infectious and fatal disease affecting equines, can be prevented and controlled through a combination of measures. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to prevent and control this disease: Vaccination Vaccination is a crucial step in preventing Glanders. Although there is no licensed vaccine available globally, some countries have developed their own vaccines. The vaccine is typically administered to horses, donkeys, and mules, and it provides immunity against the bacterium Burkholderia mallei. Vaccination programs should be implemented in areas where Glanders is endemic or where there is a high risk of transmission. Hygiene Practices Good hygiene practices are essential in preventing the spread of Glanders. Here are some measures to be taken:
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling animals or their equipment.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, and gowns when handling animals or their secretions.
- Disinfect equipment, utensils, and surfaces that come into contact with animals or their secretions.
- Avoid sharing equipment, utensils, or food and water between animals.
- Implement proper waste disposal and sanitation measures.
- Quarantine infected animals immediately, and keep them isolated from other animals.
- Restrict movement of animals from infected areas to prevent transmission to other areas.
- Implement surveillance and monitoring programs to detect and respond to outbreaks promptly.
- Restrict human movement from infected areas to prevent transmission to other areas.
- Implement proper animal importation and exportation protocols.
- Screen animals for Glanders before importation or exportation.
- Restrict animal gatherings and events in areas where Glanders is endemic or where there is a high risk of transmission.
- Implement proper animal identification and record-keeping systems.
- Educate animal owners, veterinarians, and animal handlers about the risks and consequences of Glanders.
- Provide information on prevention and control measures, including vaccination, hygiene practices, and quarantine.
- Encourage reporting of suspected cases to the relevant authorities.
- Collaborate with local communities, veterinarians, and animal health authorities to implement prevention and control measures.
What is the role of veterinarians in implementing the Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025?
Implementing the Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025: The Crucial Role of Veterinarians The Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025 is a comprehensive strategy aimed at eliminating glanders, a highly infectious and deadly disease affecting equines, from India. Veterinarians play a vital role in the successful implementation of this plan, and their responsibilities are multifaceted. Diagnosis: The First Line of Defense Veterinarians are responsible for diagnosing glanders in equines, which is a critical step in preventing the spread of the disease. They must be trained to identify the symptoms of glanders, including nasal discharge, skin lesions, and respiratory problems. A timely and accurate diagnosis enables prompt reporting and subsequent control measures, thereby preventing the disease from spreading to other animals and humans. Reporting: A Key Component of Surveillance Veterinarians are obligated to report suspected cases of glanders to the relevant authorities, including the local animal husbandry department and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR). This reporting mechanism enables the tracking of disease outbreaks, identification of hotspots, and implementation of targeted control measures. Veterinarians must maintain accurate records of suspected cases, including the animal's history, clinical signs, and laboratory test results. Awareness-Raising: Educating Stakeholders Veterinarians are also responsible for raising awareness about glanders among equine owners, breeders, and handlers. This includes educating them on the risks of the disease, its symptoms, and the importance of vaccination. Veterinarians must also disseminate information on biosecurity measures, such as proper hygiene practices, to prevent the spread of the disease. By raising awareness, veterininarians can empower stakeholders to take proactive measures to prevent glanders outbreaks. Other Key Responsibilities In addition to diagnosis, reporting, and awareness-raising, veterinarians have several other key responsibilities in implementing the Revised National Action Plan on Glanders 2025, including:
- Vaccination: Veterinarians must ensure that equines are vaccinated against glanders, as per the vaccination schedule recommended by the ICAR.
- Surveillance: Veterinarians must conduct regular surveillance in equine populations to detect early signs of glanders outbreaks.
- Research and Development: Veterinarians must contribute to research and development efforts aimed at improving diagnostic tools, vaccines, and treatment options for glanders.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Veterinarians must collaborate with other stakeholders, including animal husbandry departments, ICAR, and NGOs, to ensure a coordinated response to glanders outbreaks.
Promoted
Massive ROI on Your Career: Resume Bundle for Only ₹99
A winning resume is worth thousands in salary. Our bundle of 4,400+ templates costs just ₹99. The ROI is massive.
🔥 Get Lifetime Access Now 🔥
