Imagine waking up one morning to the news that the very foundation of our continent is slowly sinking. The thought is almost incomprehensible, and yet, it's a harsh reality that geologists have been warning us about for decades. The shocking revelation that North America is indeed sinking is a wake-up call that demands our attention, and it's essential that we delve deeper into the implications of this phenomenon. Geological warnings have been sounded for years, but they've often fallen on deaf ears. The scientific community has been monitoring the subtle changes in our planet's crust, and the data paints a dire picture. The North American tectonic plate, which spans from the west coast of California to the east coast of Newfoundland, is slowly but steadily descending into the Earth's mantle. But what does this mean, exactly? The consequences of a sinking continent are far-reaching and catastrophic. Imagine:
- Coastal cities and towns slowly disappearing beneath the waves, displacing millions of people and destroying entire ecosystems.
- Roads and infrastructure crumbling as the ground beneath them shifts and settles.
- Floods and natural disasters becoming more frequent and intense as the landscape changes.
- Drastic changes to global weather patterns, as the altered geography disrupts atmospheric circulation and ocean currents.
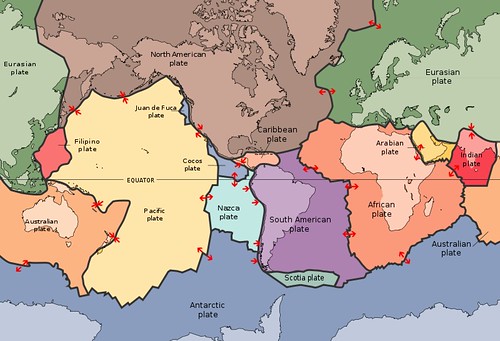
The Sinking Feeling: Understanding the Science Behind North America's Descent
- The Lake Superior region, which formed as a result of rifting and volcanic activity
- The Midcontinent Gravity High, a region of high gravity readings that indicates the presence of dense, mafic rocks
- The Illinois Basin, a large sedimentary basin that formed as a result of rifting and subsidence

Warning Signs: The Geological Evidence Pointing to an Imminent Catastrophe
- Reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and transition to renewable energy sources to reduce the strain on the planet.
- Implement sustainable water management practices to prevent groundwater depletion and land subsidence.
- Invest in early warning systems and disaster preparedness measures to save lives and reduce the economic impact of natural disasters.
- Support scientific research into the causes and consequences of geological disasters to better understand and prepare for the challenges ahead.

The Human Impact: How a Sinking North America Will Affect Our Lives
- Loss of arable land and agricultural productivity
- Disruption to food supplies and distribution networks
- Increased risk of waterborne diseases and health problems
- Mass migration and refugee crises
- Increased competition for scarce resources
- Economic instability and potential collapse of industries
- Increased risk of injury and death from natural disasters
- Exposure to waterborne diseases and health problems
- Long-term mental health impacts from displacement and trauma
- Disruption to transportation networks and supply chains
- Loss of access to essential services, such as healthcare and education
- Increased risk of power outages and communication disruptions

What's Next? The Future of North America in the Face of Geological Instability
- Seismic monitoring: tracking earthquakes and seismic activity to understand the movement of tectonic plates.
- GPS tracking: using Global Positioning System technology to measure the gradual sinking of the continent.
- Geodetic surveys: conducting regular surveys to assess the changing shape of the continent.
- Geoengineering: large-scale technological interventions in the Earth's climate and geology to counteract the effects of sinking.
- Seismic dampening: using advanced materials and structures to absorb and redirect seismic energy, reducing the impact of earthquakes.
- Artificial intelligence: leveraging AI to analyze vast amounts of data, predict geological events, and optimize mitigation strategies.
- Increased seismic activity: as the continent sinks, the likelihood of powerful earthquakes and tsunamis increases.
- Coastal erosion and flooding: rising sea levels and sinking coastlines could displace millions of people and destroy entire ecosystems.
- Economic devastation: the impact on global trade, infrastructure, and economies could be catastrophic.
- Developing and implementing effective mitigation strategies.
- Investing in research and development of geoengineering and seismic dampening technologies.
- Enhancing international cooperation and knowledge sharing to tackle this global challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is North America's sinking a natural process, or is it exacerbated by human activities?
The continent of North America is experiencing a phenomenon of gradual descent, which has sparked debate among scientists and policymakers. While natural geological processes have contributed to this sinking, human activities have undoubtedly exacerbated the issue. It is essential to understand the interplay between these factors to address the consequences of North America's descent. Geological Processes: North America's sinking can be attributed to various geological processes that have been occurring over millions of years. The continent is situated on the North American tectonic plate, which is constantly moving and interacting with other plates. This movement causes the Earth's crust to stretch, thin, and eventually sink. Additionally, the weight of the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains pushes down on the crust, contributing to the continent's descent. Groundwater Depletion: One significant human factor contributing to North America's sinking is groundwater depletion. The excessive extraction of groundwater for agricultural, industrial, and municipal purposes has led to a substantial decrease in the water table. As groundwater is pumped out, the weight of the overlying rocks and soil increases, causing the land surface to sink. This process, known as subsidence, is particularly pronounced in areas with high population density and intense agricultural activity. Climate Change: Climate change is another critical factor exacerbating North America's descent. As the planet warms, the melting of glaciers and ice sheets reduces the weight on the Earth's crust, causing it to rise in some areas. However, this process also leads to sea-level rise, which increases the pressure on coastal regions, resulting in land subsidence. Furthermore, changes in precipitation patterns and increased flooding events due to climate change accelerate soil erosion and sedimentation, contributing to the continent's descent. Other Human Factors: Several other human activities contribute to North America's sinking, including:
- Deforestation and land conversion: The removal of vegetation and conversion of natural habitats to agricultural land or urban areas increases soil erosion and reduces the land's ability to absorb water, leading to subsidence.
- Oil and gas extraction: The extraction of fossil fuels can cause the land surface to sink due to the removal of underground fluids and the resulting decrease in pressure.
- Urbanization and construction: The weight of buildings, infrastructure, and other structures can compress the soil and contribute to subsidence, particularly in areas with soft or unstable ground.
- Implementing efficient water management systems to reduce groundwater depletion
- Promoting sustainable land use practices, such as reforestation and conservation
- Investing in renewable energy sources to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels
- Developing and implementing climate-resilient infrastructure and urban planning strategies
What can individuals do to prepare for the potential catastrophe?
As the world grapples with the looming threat of catastrophes, it's essential for individuals to take proactive steps to prepare themselves and their loved ones for any eventuality. While it's impossible to predict with certainty when or where a disaster will strike, having a well-thought-out plan and adopting sustainable living practices can significantly reduce the risks and impact of a catastrophe. Emergency Preparedness Plans Creating an emergency preparedness plan is a crucial step in safeguarding your family and property. This plan should include:
- Identifying potential risks: Assess the types of disasters that are most likely to occur in your area, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, or floods.
- Designating a meeting point: Choose a safe location where family members can gather in case of separation during an emergency.
- Stocking an emergency kit: Assemble a kit with essential items like food, water, first aid supplies, and a battery-powered radio.
- Staying informed: Stay up-to-date with weather forecasts, news, and emergency alerts through a NOAA Weather Radio or a reliable news source.
- Practicing drills: Conduct regular drills with your family to ensure everyone knows what to do in case of an emergency.
- Conserving water: Implement water-saving measures like fixing leaks, using low-flow appliances, and harvesting rainwater.
- Reducing energy consumption: Switch to energy-efficient lighting, insulate your home, and use renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
- Growing your own food: Start a garden or participate in a community-supported agriculture program to ensure a steady supply of fresh produce.
- Reducing waste: Implement recycling programs, compost food waste, and avoid single-use plastics.
- Building a community network: Connect with your neighbors and community members to build a support system that can help in times of need.
- Secure your home: Ensure that your home is securely anchored to its foundation, and consider installing storm shutters or impact-resistant windows.
- Stay financially prepared: Set aside an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses and maintain a cash reserve in small bills for use during a power outage.
- Stay informed about local resources: Familiarize yourself with local emergency services, shelters, and resources like food banks and disaster relief organizations.
Are there any international efforts to address the sinking of North America?
As the crisis of North America's descent continues to unfold, the international community has recognized the urgent need for a collective response. Governments, scientists, and international organizations are coming together to develop a unified strategy for mitigating the effects of this unprecedented event. Global Response The global response to the crisis has been marked by a sense of urgency and cooperation. Governments from around the world have acknowledged the severity of the situation and are working together to share resources, expertise, and knowledge to address the crisis. The United Nations has taken a leading role in coordinating the international response, with the Secretary-General calling for a global effort to support the affected regions. Scientific Collaborations Scientists from various disciplines are working together to better understand the causes and consequences of North America's descent. International collaborations are underway to study the geological, environmental, and socio-economic impacts of the crisis. Researchers are sharing data, models, and expertise to develop more accurate predictions and to identify potential solutions. For example, the International Geophysical Union has established a task force to study the tectonic and volcanic implications of the crisis. International Organizations Several international organizations are playing a critical role in the response effort. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is providing financial assistance to affected countries, while the World Bank is supporting infrastructure development and reconstruction projects. The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is working to address the humanitarian and socio-economic impacts of the crisis, including providing aid to displaced communities and supporting sustainable development initiatives. Unified Strategy A unified strategy for mitigating the effects of North America's descent is being developed through a series of international conferences and workshops. The strategy will focus on the following key areas:
- Risk Reduction and Management**: Developing early warning systems, emergency preparedness plans, and evacuation protocols to minimize the loss of life and property.
- Infrastructure Development**: Building resilient infrastructure, including sea walls, levees, and green infrastructure, to protect communities and ecosystems from the impacts of the crisis.
- Climate Change Adaptation**: Supporting climate-resilient agriculture, water management, and urban planning to help communities adapt to the changing environment.
- Humanitarian Response**: Providing aid, shelter, and support to displaced communities, and addressing the humanitarian and socio-economic impacts of the crisis.
- Research and Development**: Continuing to study the causes and consequences of the crisis, and developing new technologies and solutions to mitigate its effects.
Promoted
Massive ROI on Your Career: Resume Bundle for Only ₹99
A winning resume is worth thousands in salary. Our bundle of 4,400+ templates costs just ₹99. The ROI is massive.
🔥 Get Lifetime Access Now 🔥
