As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, energy security, and environmental sustainability, the role of transportation in the energy mix has come under scrutiny. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of biofuels, particularly ethanol, as a cleaner and more environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) have been at the forefront of this movement, touting the benefits of higher ethanol blends in fuel. One of the most contentious claims made by OMCs is that a higher ethanol blend in fuel has no significant impact on vehicle fuel efficiency. This claim has sparked intense debate among stakeholders, with some arguing that higher ethanol blends can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, while others claim that the impact is negligible. As we delve into the world of biofuels and their impact on vehicle performance, it is essential to separate fact from fiction and examine the evidence behind the claims made by OMCs. So, what exactly is ethanol, and how does it affect vehicle fuel efficiency? Ethanol is a biofuel produced from fermented plant materials, such as corn, sugarcane, or switchgrass. When blended with gasoline, ethanol can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. However, ethanol contains less energy per unit volume than gasoline, which means that more volume is required to achieve the same level of energy output. This raises concerns about the potential impact of higher ethanol blends on fuel efficiency. OMCs argue that modern vehicles are designed to accommodate higher ethanol blends without sacrificing fuel efficiency. They point to studies that show minimal differences in fuel economy between E10 (10% ethanol, 90% gasoline) and E15 (15% ethanol, 85% gasoline) blends. However, critics argue that these studies are often based on laboratory tests or small-scale trials, and may not reflect real-world driving conditions. Moreover, there are concerns about the potential impact of higher ethanol blends on older vehicles, which may not be equipped with the necessary technology to handle the higher ethanol content. Some of the key factors that influence the impact of ethanol blends on fuel efficiency include:
- Vehicle type and age: Newer vehicles with advanced engine technologies may be more efficient at handling higher ethanol blends, while older vehicles may experience a decrease in fuel efficiency.
- Driving habits: Aggressive driving, such as rapid acceleration and braking, can reduce fuel efficiency, regardless of the ethanol blend.
- Climate and geography: Extreme temperatures, high altitudes, and hilly terrain can all impact fuel efficiency, and may be exacerbated by higher ethanol blends.
- Engine calibration: The way an engine is calibrated to run on a particular fuel blend can significantly impact fuel efficiency.
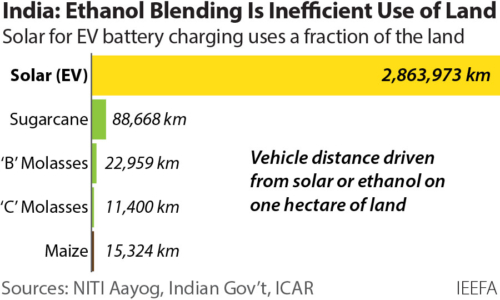
The Ethanol Blend Conundrum
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Ethanol is a biofuel produced from renewable sources such as sugarcane, corn, and other biomass. It emits significantly less greenhouse gases compared to traditional fossil fuels, making it a cleaner and more environmentally friendly option.
- Energy Security: By blending ethanol with gasoline, India can reduce its dependence on imported fossil fuels, improving energy security and reducing the burden on the country's foreign exchange reserves.
- Boost to Agriculture: The increased demand for ethanol will provide a new market for farmers, particularly sugarcane farmers, and create new employment opportunities in the agricultural sector.
- Reduced Fuel Economy: Vehicles may experience a reduction in fuel economy, leading to higher fuel costs for consumers.
- Engine Modifications: The higher ethanol content may require modifications to vehicle engines, which could add to the cost of vehicle ownership.
- Compatibility Issues: Some older vehicles may not be compatible with higher ethanol blends, which could lead to engine damage or other performance issues.
OMCs' Stance on Fuel Efficiency
- Reduced Fuel Costs: Ethanol is generally cheaper to produce than gasoline, which means that increasing the ethanol content in fuel could lead to lower fuel costs for consumers.
- Improved Environmental Performance: Ethanol is a renewable energy source that produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than gasoline, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
- Enhanced Energy Security: By increasing the use of domestically produced ethanol, countries can reduce their reliance on imported oil and enhance their energy security.
- Support for Agriculture: The production of ethanol from biomass sources such as corn and sugarcane provides a new market for agricultural products, supporting rural development and the agricultural sector.

The Science Behind Ethanol Blending
- Reduced particulate matter emissions
- Lower carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions
- Increased engine power and efficiency
- Advanced fuel injection systems to optimize fuel spray patterns
- Turbocharging and direct injection to enhance power density and efficiency
- Exhaust gas recirculation to reduce emissions and improve combustion
- Enhance fuel stability and prevent phase separation
- Inhibit corrosion and wear on engine components
- Improve fuel flow and lubricity
The Way Forward: Balancing Fuel Efficiency and Sustainability
- In addition to setting targets, governments can also provide incentives for the production and use of ethanol-blended fuels. Tax credits, grants, and low-interest loans can help to offset the costs of production and infrastructure development.
- Moreover, governments can implement policies to encourage the adoption of flex-fuel vehicles, which can run on higher blends of ethanol. This can be achieved through tax incentives, rebates, or other financial incentives for consumers who purchase flex-fuel vehicles.
- Public awareness campaigns can help to educate consumers about the benefits of ethanol-blended fuels and the role they can play in reducing their carbon footprint.
- Automakers and fuel retailers can also play a critical role in educating consumers by providing clear labeling and information about the ethanol content of fuels.
- Furthermore, consumer incentives, such as discounts or rewards programs, can encourage consumers to choose ethanol-blended fuels over traditional fossil fuels.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the current ethanol blend percentage in Indian fuels?
The Indian government has been actively promoting the use of ethanol-blended fuels as a cleaner and more environment-friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. In recent years, there has been a significant push to increase the ethanol blend percentage in Indian fuels, with the aim of reducing the country's dependence on imported oil and mitigating the impact of climate change. Currently, the ethanol blend percentage in Indian fuels stands at 8.5%. This means that for every 100 liters of petrol sold in the country, 8.5 liters is ethanol. This blend percentage is set by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, which is responsible for regulating the fuel industry in India. The 8.5% blend percentage is applicable to all types of petrol, including regular, premium, and high-octane fuels. However, the Indian government has ambitious plans to increase the ethanol blend percentage in the coming years. The target is to reach an ethanol blend percentage of 20% by 2025, which is expected to reduce the country's dependence on imported oil by up to 20%. To achieve this target, the government is taking several steps, including:
- Encouraging sugar mills and other ethanol producers to increase production capacity
- Providing incentives to oil marketing companies to blend more ethanol with petrol
- Investing in infrastructure to improve ethanol transportation and storage
- Developing new technologies to improve ethanol production efficiency and reduce costs
How does ethanol blending affect vehicle performance?
The increasing use of ethanol-blended fuels has sparked a heated debate among car enthusiasts and environmentalists alike. As governments worldwide promote the use of biofuels to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, it's essential to understand how ethanol blending affects vehicle performance. In this article, we'll delve into the impact of ethanol blending on power, torque, and fuel efficiency. Power Output Ethanol-blended fuels contain a percentage of ethanol, typically ranging from 5% to 15% (E5 to E15). This blend can affect an engine's power output in several ways. Ethanol contains less energy density than gasoline, which means it takes more volume to produce the same amount of power. As a result, engines running on ethanol-blended fuels may experience a slight decrease in power output, particularly during high-performance driving or when towing heavy loads. However, modern engines are designed to adapt to the energy density of ethanol-blended fuels. Many vehicles, especially those manufactured after 2007, have engine control units (ECUs) that can adjust fuel injection and ignition timing to compensate for the lower energy density of ethanol. This adaptation minimizes the impact on power output, ensuring a smoother driving experience. Torque and Engine Performance Torque, or rotational force, is another critical aspect of engine performance affected by ethanol blending. Ethanol's higher octane rating can help to reduce engine knocking or pinging, which can increase torque and overall engine performance. However, the lower energy density of ethanol can also lead to a slight decrease in torque, particularly at lower engine speeds. The impact of ethanol blending on torque is more pronounced in smaller engines or those with higher compression ratios. In these cases, the engine may struggle to produce the same level of torque as it would on traditional gasoline. However, many modern engines are designed with advanced technologies, such as turbocharging or direct fuel injection, which can help mitigate the effects of ethanol blending on torque. Fuel Efficiency Fuel efficiency is a critical concern for many vehicle owners, and ethanol blending can have both positive and negative effects on this aspect of vehicle performance. On the one hand, ethanol contains less energy density than gasoline, which means that more fuel volume is required to achieve the same distance. This can result in decreased fuel efficiency, particularly during city driving or stop-and-go traffic. On the other hand, many modern engines are optimized to run on ethanol-blended fuels, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency. The higher octane rating of ethanol can help to reduce engine knocking and improve combustion efficiency, resulting in better fuel economy. Additionally, some vehicles are designed with advanced technologies, such as cylinder deactivation or start-stop systems, which can help to minimize the impact of ethanol blending on fuel efficiency. Other Factors to Consider While power output, torque, and fuel efficiency are the most significant aspects of vehicle performance affected by ethanol blending, there are other factors to consider:
- Engine durability: Ethanol can be corrosive to engine components, particularly fuel system components, which can lead to premature wear and tear.
- Fuel system compatibility: Some older vehicles may not be compatible with higher blends of ethanol, which can lead to fuel system damage or engine failure.
- Cold-start performance: Ethanol-blended fuels can be more difficult to ignite in cold temperatures, which can affect cold-start performance.
- Vehicle maintenance: Ethanol-blended fuels can require more frequent fuel filter replacements and spark plug maintenance due to their corrosive properties.
Are higher ethanol blends compatible with all vehicles?
As the world shifts towards more environmentally friendly fuel options, higher ethanol blends have become a topic of discussion. With the increasing popularity of E15, E30, and even E85 fuel, many vehicle owners are left wondering if these higher ethanol blends are compatible with all vehicles. The answer is not a simple yes or no, as compatibility varies greatly depending on the type of vehicle, its age, and its engine specifications. Older Vehicles (Pre-2001) Vehicles manufactured before 2001 are generally not compatible with higher ethanol blends. The reason lies in the materials used in the engine and fuel system of these older vehicles. Many of these vehicles have fuel tanks, fuel lines, and engine components made from materials that can be damaged or corroded by higher ethanol concentrations. Using higher ethanol blends in these vehicles can lead to engine knock, decreased fuel efficiency, and even engine failure. Model Years 2001-2011 Vehicles manufactured between 2001 and 2011 are a mixed bag when it comes to higher ethanol blends. While some models can handle E15, others may not be compatible. It's essential to check the vehicle's owner's manual or consult with the manufacturer to determine the recommended fuel type. Some vehicles from this era may have engine components that can tolerate E15, but it's still crucial to exercise caution and follow the manufacturer's guidelines. Modern Vehicles (2012 and Newer) Most vehicles manufactured in 2012 and later are designed to be compatible with E15. In fact, many automakers have explicitly stated that their vehicles can run on E15. However, it's still important to check the owner's manual or consult with the manufacturer to confirm compatibility. Some modern vehicles may even be compatible with higher ethanol blends like E30 or E85, but this is typically limited to flex-fuel vehicles (FFVs). Specialized Engines Certain specialized engines, such as those found in:
- High-performance vehicles
- Marine engines
- Small engines (e.g., lawn mowers, generators)
- Classic cars

