The cosmos has long been a realm of mystery and wonder, with new discoveries continually expanding our understanding of the universe. One such recent finding has sent shockwaves through the scientific community, as NASA's James Webb Telescope has identified a peculiar comet that is redefining our knowledge of these icy bodies. Comet 3I/ATLAS, as it has been designated, was first detected in December 2022 by the James Webb Telescope, a space observatory that has been instrumental in uncovering the secrets of the cosmos. This remarkable discovery has provided scientists with a unique opportunity to study a comet up close, revealing some extraordinary characteristics that set it apart from its peers. One of the most striking features of Comet 3I/ATLAS is its unusual shape. Unlike typical comets, which are often depicted as spherical or oval in shape, this comet has a more elongated, irregular form. This unusual morphology has sparked intense interest among astronomers, who are eager to understand the processes that have shaped this comet's development. Another notable aspect of Comet 3I/ATLAS is its unprecedented brightness. As it approaches the inner solar system, the comet is emitting an extraordinary amount of light, making it one of the brightest comets ever recorded. This increased luminosity has enabled scientists to study the comet in unprecedented detail, gaining insights into its composition and behavior. Some of the key characteristics of Comet 3I/ATLAS include:
- Its highly elliptical orbit, which takes it from the outer reaches of the solar system to within 23 million miles of the sun.
- A highly active surface, with intense outgassing and dust emission.
- A unique chemical composition, featuring a high concentration of organic molecules.
- A small size, with estimates suggesting a diameter of approximately 1 mile.

What is Comet 3I/ATLAS?
- Methanol: a key component of cometary ices, which plays a crucial role in the comet's outgassing process.
- Ethanol: a complex organic molecule that's rarely detected in comets.
- Carbon dioxide: a significant component of the comet's gas, which is unusual for an Oort Cloud comet.

The James Webb Telescope's Role in the Discovery
- High-resolution imaging: The telescope's 6.5-meter primary mirror and advanced optics enable it to capture stunning images of celestial objects with unprecedented clarity.
- Spectroscopy: The telescope can analyze the light emitted by objects, providing valuable information about their composition, temperature, and velocity.
- Cryogenic cooling: The telescope's instruments are cooled to extremely low temperatures, allowing them to detect faint signals from distant objects.
- Orbit around the L2 point: The telescope's orbit around the Lagrange point 2 (L2) provides a stable thermal environment, minimizing thermal noise and allowing for more accurate observations.
- Unprecedented brightness: Comet 3I/ATLAS is one of the brightest comets ever observed, with a magnitude of -10, making it visible to the naked eye.
- Asymmetric coma: The comet's coma, or atmosphere, is asymmetrical, with a bright tail and a fainter leading edge.
- Unusual composition: Spectroscopic analysis revealed that the comet's composition is distinct from other comets, with a higher abundance of organic molecules and a lack of typical comet emissions.
- Orbital peculiarities: Comet 3I/ATLAS has a highly elliptical orbit, taking it from the outer reaches of the solar system to a perihelion (closest point to the Sun) of just 1.3 astronomical units (AU).
The Eccentric Behaviour of Comet 3I/ATLAS
- Gravitational Interactions: One possibility is that the comet's orbit has been influenced by the gravitational pull of nearby planets, particularly Jupiter. The massive planet's gravity could have perturbed the comet's trajectory, causing it to follow an elliptical path.
- Close Encounters: Another theory suggests that Comet 3I/ATLAS may have had close encounters with other celestial bodies in the past, such as asteroids or other comets. These encounters could have altered the comet's orbit, resulting in its unusual pattern.
- Original Orbit: Some scientists believe that Comet 3I/ATLAS may have originated from the Oort Cloud, a distant region of icy bodies surrounding our solar system. The comet's eccentric orbit could be a remnant of its original trajectory from the Oort Cloud.
- Yarkovsky Effect: The Yarkovsky effect is a phenomenon where the comet's rotation and thermal properties cause it to experience a continuous force, which can alter its orbit over time. This effect could be contributing to the comet's eccentric behavior.

Implications of the Discovery and Future Research
- Compositional Analysis: Further study of the comet's composition will provide valuable insights into the early solar system's chemistry and the origins of life on Earth.
- Orbital Dynamics: Researchers will continue to study the comet's orbit, gaining a deeper understanding of the gravitational forces that shape the solar system.
- Comparative Planetology: The discovery of comet 3I/ATLAS has sparked interest in the potential for similar comets in other planetary systems, with scientists exploring the possibility of discovering exocomets.
- The Search for Other Long-Period Comets: The detection of comet 3I/ATLAS has raised hopes of discovering other long-period comets, which could provide further insights into the early solar system.
- Organic Molecules: The comet's composition may reveal the presence of organic molecules, which are building blocks of life.
- Water Delivery: Further research may confirm that comets like 3I/ATLAS played a significant role in delivering water to Earth, paving the way for life to emerge.
- New Insights into the Oort Cloud: The discovery of comet 3I/ATLAS has sparked interest in the Oort Cloud, with scientists hoping to learn more about this enigmatic region of the solar system.
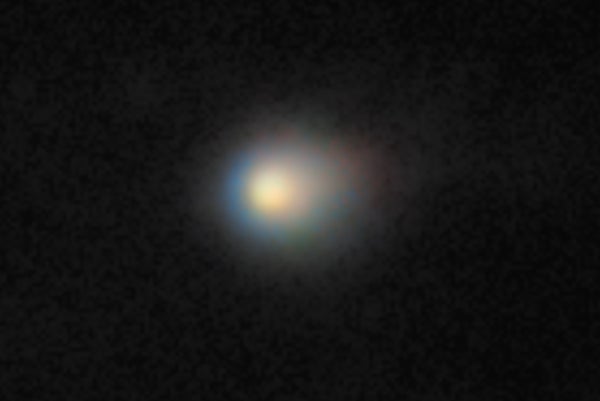

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What makes comet 3I/ATLAS an 'alien' comet?
Comet 3I/ATLAS, discovered in 2019, has garnered significant attention among astronomers and scientists due to its unusual composition and origin. This "alien" comet, as it's been dubbed, exhibits distinct characteristics that set it apart from typical comets. Composition: A Key Differentiator Comet 3I/ATLAS's composition is one of its most striking features. Unlike typical comets, which are primarily composed of water ice, 3I/ATLAS is rich in carbon dioxide (CO2) and organic compounds. These organic compounds, including complex molecules like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), are commonly found in interstellar space and are believed to be building blocks of life. The presence of these compounds in 3I/ATLAS suggests that it may have formed in a region of the solar system with a unique chemistry. Origin: A Mysterious Past The origin of comet 3I/ATLAS is another aspect that sets it apart from typical comets. Most comets originate from the Oort Cloud, a distant, spherical shell of icy bodies surrounding the solar system. However, 3I/ATLAS's orbit suggests that it may have come from a different source, potentially the scattered disc, a region of the solar system that is thought to be the source of many short-period comets. This unusual origin may have contributed to the comet's distinct composition. Differences from Typical Comets The composition and origin of comet 3I/ATLAS are not the only factors that distinguish it from typical comets. Some of the key differences include:
- Unusual Spectral Signature: 3I/ATLAS exhibits a unique spectral signature, which is different from that of typical comets.
- Higher CO2 Content: Comet 3I/ATLAS has a higher CO2 content than typical comets, which is indicative of a different formation mechanism.
- Lack of Typical Comet Features: 3I/ATLAS lacks the typical comet features, such as a prominent tail and a bright coma.
How does the James Webb Telescope's detection of comet 3I/ATLAS advance our understanding of the universe?
The detection of comet 3I/ATLAS by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) marks a significant milestone in the field of astronomy, offering valuable insights into the mysteries of our universe. This groundbreaking discovery has far-reaching implications, advancing our understanding of the cosmos in several ways. Comet 3I/ATLAS: A Unique Celestial Body Comet 3I/ATLAS is an unusual comet, characterized by its highly eccentric orbit and unprecedented brightness. This comet's detection by JWST has provided astronomers with a rare opportunity to study a comet in unprecedented detail. The telescope's advanced instrumentation has captured high-resolution images and spectra of the comet, revealing valuable information about its composition, structure, and behavior. Advancing Our Understanding of Cometary Science The JWST's detection of comet 3I/ATLAS has made significant contributions to the field of cometary science. By studying this comet, scientists can gain insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. The comet's composition and structure provide clues about the early days of our solar system, shedding light on the processes that shaped the planets and other celestial bodies. Furthermore, the study of comet 3I/ATLAS can help astronomers better understand the role of comets in delivering organic molecules and water to early Earth, potentially influencing the origins of life. Insights into the Early Universe The detection of comet 3I/ATLAS has also provided valuable insights into the early universe. The comet's highly eccentric orbit suggests that it may have originated from the Oort Cloud, a distant, spherical shell of icy bodies surrounding our solar system. This discovery has implications for our understanding of the Oort Cloud's structure and evolution, as well as the formation of long-period comets. Additionally, the study of comet 3I/ATLAS can offer insights into the early universe's chemical composition and the processes that governed the formation of the first stars and galaxies. Advancements in Telescope Technology The JWST's detection of comet 3I/ATLAS demonstrates the telescope's unparalleled capabilities and sensitivity. The telescope's advanced instrumentation, including its Cryogenic Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), have enabled scientists to capture high-resolution images and spectra of the comet. This achievement highlights the JWST's potential to make groundbreaking discoveries in various areas of astronomy, from the study of exoplanet atmospheres to the investigation of distant galaxies. Implications for Future Research The detection of comet 3I/ATLAS by the JWST has opened up new avenues for future research. Astronomers can now use the telescope to study other comets and celestial bodies in unprecedented detail, potentially leading to new discoveries and a deeper understanding of the universe. Furthermore, the JWST's capabilities will enable scientists to investigate the formation and evolution of our solar system, as well as the origins of life on Earth.
- Key Takeaways:
- The detection of comet 3I/ATLAS by the JWST has advanced our understanding of cometary science and the early universe.
- The study of comet 3I/ATLAS has provided insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
- The JWST's capabilities have demonstrated its potential to make groundbreaking discoveries in various areas of astronomy.
Will comet 3I/ATLAS pose a threat to Earth or other planets?
Comet 3I/ATLAS: A Harmless Visitor to Our Cosmic Neighborhood As Comet 3I/ATLAS makes its way through our solar system, concerns have been raised about its potential impact on Earth and other planets. With sensationalized media reports and doomsday predictions circulating online, it's essential to separate fact from fiction and provide reassurance about the comet's harmless nature. Orbital Path and Distance Comet 3I/ATLAS is currently following an elliptical orbit that will bring it closest to the Sun (perihelion) in May 2023. At its closest point, the comet will be about 100 million miles (160 million kilometers) from Earth, which is roughly 400 times the distance between our planet and the Moon. This vast distance ensures that the comet poses no threat of collision or significant gravitational disruption to our planet. Size and Composition Comet 3I/ATLAS is a relatively small comet, measuring approximately 1 mile (1.6 kilometers) in diameter. Its composition is primarily made up of ice, dust, and rocky particles, which will likely vaporize and disintegrate as it approaches the Sun. This process, known as outgassing, will create a bright tail of gas and dust, making the comet visible from Earth, but it won't have any significant effects on our planet's atmosphere or surface. Potential Effects on Other Planets While Comet 3I/ATLAS won't pose a threat to Earth, some have wondered about its potential impact on other planets in our solar system. The comet's trajectory will take it close to Jupiter's orbit, but it will not collide with the gas giant. In fact, Jupiter's massive gravity will actually help perturb the comet's orbit, ensuring it remains on a safe course. The comet will also pass near Mars' orbit, but its distance from the Red Planet will be too great to cause any significant effects. Astronomical Significance Comet 3I/ATLAS presents a unique opportunity for astronomers to study a relatively rare type of comet known as a long-period comet. These comets take more than 200 years to complete an orbit around the Sun, providing scientists with valuable insights into the early formation and evolution of our solar system. By studying Comet 3I/ATLAS, researchers can gain a better understanding of the composition and behavior of these enigmatic celestial bodies. Conclusion In conclusion, Comet 3I/ATLAS is a harmless visitor to our cosmic neighborhood. Its orbital path, size, and composition ensure that it poses no threat to Earth or other planets in our solar system. Instead, this comet offers a fascinating opportunity for scientific discovery and observation. So, mark your calendars for May 2023 and get ready to enjoy a spectacular celestial display, free from any concerns about the comet's potential impact. Key Takeaways:
- Comet 3I/ATLAS will pass within 100 million miles of Earth, posing no threat of collision or significant gravitational disruption.
- The comet's small size and composition make it harmless to our planet's atmosphere and surface.
- Jupiter's gravity will perturb the comet's orbit, ensuring it remains on a safe course.
- Comet 3I/ATLAS presents a unique opportunity for astronomers to study a rare type of long-period comet.

