In the realm of artificial intelligence, few concepts have garnered as much attention and fascination as AI agents. These intelligent entities have the potential to revolutionize numerous industries and aspects of our lives, making it essential to understand their capabilities, applications, and future implications.
Defining AI Agents
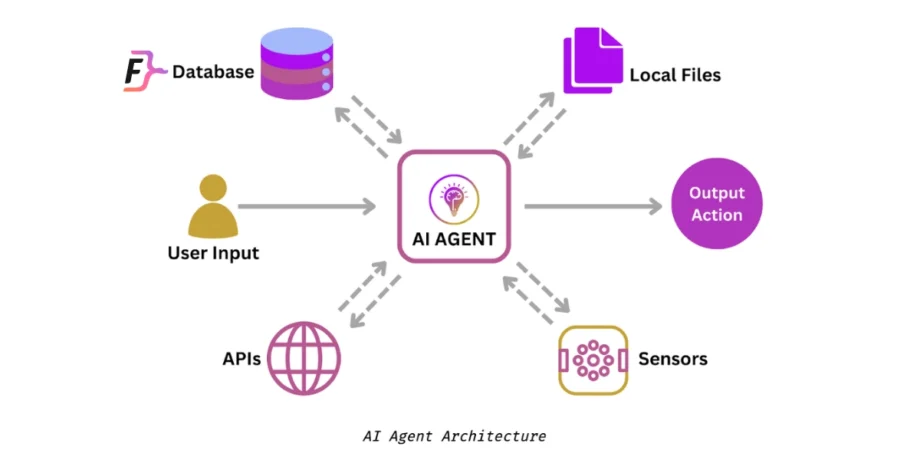
At its core, an AI agent is a program or system that perceives its environment, reasons about the current state of the environment, and takes actions to achieve a specific goal or set of goals. These agents can be simple or complex, ranging from chatbots that provide customer support to autonomous vehicles that navigate through complex traffic scenarios. The common thread among all AI agents is their ability to interact with their environment, make decisions, and adapt to new situations.Capabilities of AI Agents
AI agents possess a range of capabilities that enable them to perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. Some of the key capabilities include:- Perception: AI agents can perceive their environment through sensors, cameras, or other data sources, allowing them to gather information and make informed decisions.
- Reasoning: These agents can reason about the data they've collected, making decisions based on that information and adapting to new situations.
- Autonomy: AI agents can operate independently, making decisions and taking actions without human intervention.
- Learning: Many AI agents can learn from their experiences, improving their performance over time and adapting to new scenarios.
Applications of AI Agents
The applications of AI agents are vast and varied, with the potential to transform numerous industries and aspects of our lives. Some of the most promising applications include:- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, helping to resolve issues and improve customer satisfaction.
- Healthcare: AI agents can help diagnose diseases, develop personalized treatment plans, and assist with medical research.
- Finance: These agents can analyze financial data, detect anomalies, and make predictions about market trends.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles and drones can revolutionize the way we travel and transport goods.
Future Implications of AI Agents
As AI agents continue to evolve and improve, they will have a profound impact on our lives and the world around us. Some of the potential implications include:- Job Displacement: The automation of certain tasks may lead to job displacement, requiring workers to adapt to new roles and industries.
- Increased Efficiency: AI agents can streamline processes, reducing costs and increasing productivity in various industries.
- Improved Decision-Making: These agents can provide insights and recommendations, enabling humans to make more informed decisions.
- New Business Models: AI agents will give rise to new business models and opportunities, such as personalized services and data-driven products.

Understanding AI Agents: Definition and Core Principles
Defining AI Agents and Differentiating from Other AI Technologies
In the realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI), the term "agent" is often used to describe a specific type of AI system. But what exactly is an AI agent, and how does it differ from other AI technologies like chatbots? To answer this, let's start with a definition. An AI agent is a computer program that can perceive its environment, reason about the current state of the environment, and take actions to achieve a goal or set of goals. In essence, an AI agent is a autonomous entity that can interact with its environment, make decisions, and adapt to changes. One of the key differences between AI agents and other AI technologies like chatbots is autonomy. Chatbots, for example, are typically rule-based systems that respond to user input based on pre-defined rules. They don't have the ability to perceive their environment or make decisions independently. AI agents, on the other hand, have a degree of autonomy, allowing them to make decisions and take actions without human intervention.- Perception: This component allows the agent to perceive its environment through sensors or other data sources. The agent can gather information about its surroundings, such as visual, auditory, or tactile data.
- Reasoning: This component enables the agent to interpret the data gathered through perception and make decisions based on that data. The agent can use various reasoning techniques, such as rule-based systems, decision trees, or machine learning algorithms.
- Action: This component allows the agent to take actions in its environment based on the decisions made through reasoning. The agent can interact with its environment through actuators, such as motors, displays, or speakers.
- Learning: This component enables the agent to learn from its experiences and adapt to changes in its environment. The agent can use various learning techniques, such as machine learning, reinforcement learning, or deep learning.
Types of AI Agents
There are several types of AI agents, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The main types of AI agents are reactive, deliberative, and hybrid.- Reactive Agents: These agents respond to the current state of the environment without considering future consequences. They are typically used in applications where fast response times are critical, such as in real-time systems or robotics.
- Deliberative Agents: These agents consider future consequences of their actions and plan accordingly. They are typically used in applications where complex decision-making is required, such as in expert systems or planning systems.
- Hybrid Agents: These agents combine the strengths of reactive and deliberative agents. They can respond quickly to changes in the environment while also considering future consequences. Hybrid agents are often used in applications where both reactive and deliberative capabilities are required, such as in autonomous vehicles or smart homes.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents: Across Diverse Industries
Enhancing Customer Experience with AI Agents
One of the most prominent applications of AI agents is in customer service, where they are being used to create personalized and efficient experiences. Chatbots and virtual assistants, powered by AI, are increasingly being used to:- Provide 24/7 support to customers, reducing wait times and improving response rates.
- Offer personalized recommendations and solutions based on customer preferences and behavior.
- Streamline customer interactions by automating routine tasks and freeing up human representatives to focus on complex issues.
Transforming Healthcare with AI Agents
AI agents are also being used to transform the healthcare industry by providing diagnosis support and enabling personalized medicine. For example:- Ai-powered diagnostic tools are being used to analyze medical images and identify patterns, enabling doctors to make more accurate diagnoses.
- AI agents are being used to analyze patient data and provide personalized treatment recommendations, taking into account individual characteristics and medical histories.
- Virtual assistants are being used to monitor patient health and provide timely interventions, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
Optimizing Finance with AI Agents
AI agents are being used in the finance sector to detect fraud, optimize trading, and improve risk management. For instance:- Ai-powered systems are being used to analyze large datasets and identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activity, reducing the risk of financial losses.
- Algorithmic trading platforms powered by AI agents are being used to execute trades at high speeds and optimize portfolio performance.
- AI agents are being used to analyze market data and provide predictive insights, enabling financial institutions to make more informed investment decisions.
Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chain Optimization
Finally, AI agents are being used to optimize manufacturing processes and supply chain management. For example:- Ai-powered predictive maintenance tools are being used to predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
- AI agents are being used to optimize supply chain logistics, ensuring that products are delivered to customers on time and reducing inventory costs.
- AI-powered quality control systems are being used to inspect products and identify defects, reducing waste and improving product quality.
The Benefits and Challenges of Implementing AI Agents
Benefits of AI Agents
The integration of AI agents can yield significant benefits, including:- Increased Efficiency: AI agents can automate repetitive and mundane tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative endeavors. By streamlining processes, businesses can reduce the time spent on administrative tasks, leading to improved productivity and faster response times.
- Cost Reduction: By automating tasks and reducing the need for human intervention, businesses can significantly lower operational costs. AI agents can also help identify areas of inefficiency, enabling companies to optimize resources and minimize waste.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI agents can analyze vast amounts of data, providing actionable insights that inform better decision-making. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, businesses can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and make data-driven decisions.
Challenges of AI Agents
While the advantages of AI agents are undeniable, there are several challenges that businesses must address during implementation:Data Privacy Concerns
- Data Security: AI agents rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively. However, this data can be sensitive, and its misuse can have severe consequences. Ensuring the security and integrity of data is crucial to maintaining trust and avoiding reputational damage.
- Privacy Regulations: With the introduction of regulations like GDPR and CCPA, businesses must ensure that their AI agents comply with privacy laws and regulations. Failure to do so can result in significant fines and legal repercussions.
Ethical Considerations
- Bias and Fairness: AI agents can perpetuate biases and discrimination if they're trained on flawed or biased data. It's essential to ensure that AI systems are fair, transparent, and unbiased, avoiding harm to marginalized groups.
- Accountability and Transparency: As AI agents make decisions, it's crucial to establish accountability and transparency mechanisms. This includes explaining the reasoning behind AI-driven decisions and ensuring that humans are involved in the decision-making process.
Integration Complexities
- Technical Complexity: Integrating AI agents with existing systems can be a complex and time-consuming process. Ensuring seamless integration requires significant technical expertise and resources.
- Cultural and Organizational Change: The implementation of AI agents often requires significant cultural and organizational changes. Businesses must be prepared to adapt and evolve to maximize the benefits of AI adoption.

The Future of AI Agents: Trends and Predictions
- Multi-Agent Systems (MAS): These systems comprise multiple AI agents that interact and coordinate with each other to achieve a common goal. MAS has applications in areas like supply chain management, traffic control, and smart cities.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): This machine learning approach enables AI agents to learn from their interactions with the environment and make decisions based on rewards or penalties. RL has been successfully applied in fields like robotics, game playing, and autonomous vehicles.
- Bias in AI Decision-Making: AI agents can perpetuate biases present in the data used to train them, leading to unfair outcomes. It's crucial to develop mechanisms to detect and mitigate bias in AI decision-making.
- Accountability and Transparency: With autonomous AI agents, it's challenging to determine who is accountable for their actions. There must be a clear understanding of how AI agents arrive at their decisions and a framework for accountability.
Healthcare
AI agents will improve patient care by analyzing medical data, identifying patterns, and providing personalized treatment recommendations.Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots will become increasingly prevalent, offering 24/7 customer support and streamlining customer interactions.Transportation
Autonomous vehicles, enabled by AI agents, will transform the transportation industry, increasing safety, reducing traffic congestion, and enhancing mobility for the elderly and disabled. As AI agents continue to evolve, it's essential to prioritize responsible development, deployment, and governance. By doing so, we can harness the potential of AI agents to drive innovation, productivity, and societal progress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between an AI agent and a chatbot?
Defining the Boundaries: AI Agents vs. Chatbots
When it comes to artificial intelligence, two terms are often used interchangeably: AI agents and chatbots. However, these two entities serve distinct purposes and possess unique characteristics. While chatbots are designed to engage in conversation, AI agents are capable of much more. In this section, we'll delve into the differences between these two AI-powered entities and explore the broader capabilities of AI agents. Chatbots: Limited yet Effective Chatbots are designed to simulate human-like conversations, typically within a specific scope or domain. They are programmed to respond to user input, providing answers or guidance on a particular topic. Chatbots are ideal for handling customer inquiries, booking appointments, or providing simple support. Their capabilities are largely limited to conversational interactions, making them an excellent choice for tasks that require a human touch without the need for complex problem-solving. AI Agents: Intelligent and Autonomous AI agents, on the other hand, are more advanced entities that possess the ability to perform complex tasks, learn from experience, and adapt to new situations. They are designed to operate autonomously, making decisions and taking actions based on their programming and data analysis. AI agents can:- Process and analyze large datasets to identify patterns and trends
- Learn from experience and improve their performance over time
- Make decisions and take actions independently, without human intervention
- Interact with other systems and devices to achieve a common goal
Are AI agents safe and ethical to use?
As AI agents become increasingly pervasive in various aspects of our lives, concerns about their safety and ethical implications have grown. It's essential to address these concerns and propose solutions to ensure responsible development and deployment of AI systems.
Bias in AI Agents
One of the primary concerns surrounding AI agents is bias. Biased AI systems can perpetuate and even amplify existing social inequalities, leading to unfair outcomes and discriminatory practices. Bias can be introduced through various factors, such as:- Imbalanced or incomplete training data
- Insufficient diversity in development teams
- Inadequate testing and validation
- Use diverse and representative training data
- Implement robust testing and validation protocols
- Establish diverse development teams with diverse perspectives
- Regularly audit and update AI systems to detect and correct bias
Transparency and Explainability
Another critical concern is the lack of transparency and explainability in AI decision-making processes. Opaque AI systems can lead to a lack of trust and accountability, making it challenging to identify and address errors or biases. To promote transparency and explainability, developers should:- Design AI systems with interpretability in mind
- Implement techniques like model interpretability and feature attribution
- Provide clear explanations for AI-driven decisions and actions
- Establish transparent and accessible auditing and reporting mechanisms
Accountability and Responsibility
As AI agents become more autonomous, questions arise about accountability and responsibility in case of errors or adverse outcomes. Clear accountability mechanisms are essential to ensure that developers, users, and other stakeholders are held responsible for AI-driven actions. To establish accountability, it's crucial to:- Define and assign clear roles and responsibilities
- Establish robust error detection and reporting mechanisms
- Implement transparent and accessible logging and auditing systems
- Develop and implement standards for AI system safety and security
Potential Misuse of AI Agents
The potential misuse of AI agents is a significant concern, particularly in areas like cybersecurity, surveillance, and autonomous weapons. Malicious AI use can have devastating consequences, including compromised privacy, security breaches, and even loss of life. To prevent misuse, it's essential to:- Develop and implement strict regulations and governance frameworks
- Establish international agreements and standards for AI development and use
- Conduct regular risk assessments and impact analyses
- Invest in AI-specific cybersecurity measures and countermeasures
How can businesses benefit from implementing AI agents?
Implementing AI agents can bring about a transformative change in the way businesses operate, leading to significant returns on investment (ROI). By automating repetitive tasks, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing customer experience, AI agents can help businesses reap substantial benefits.
Increased Efficiency
AI agents can process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, freeing up human resources to focus on higher-value tasks. By automating mundane tasks, businesses can:- Reduce manual errors and inconsistencies
- Streamline processes, leading to faster turnaround times
- Enhance productivity, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives
Cost Savings
The implementation of AI agents can result in significant cost savings for businesses. By automating tasks and processes, companies can:- Reduce labor costs associated with manual processing
- Minimize the need for overtime and temporary staff
- Decrease infrastructure costs, such as hardware and software maintenance
- Optimizing resource allocation and utilization
- Identifying areas of inefficiency and waste
- Providing predictive maintenance and reducing downtime
Improved Customer Experience
AI agents can revolutionize the way businesses interact with their customers, providing personalized and efficient support. By implementing AI-powered chatbots, businesses can:- Offer 24/7 customer support, reducing wait times and increasing satisfaction
- Provide personalized recommendations and offers, enhancing the customer experience
- Analyze customer feedback and sentiment, enabling data-driven decision-making
- Streamlining the onboarding process, reducing friction and increasing engagement
- Offering proactive support, anticipating and resolving issues before they escalate
- Providing omnichannel support, ensuring a seamless customer experience across all touchpoints

